Overview
- Peptide EKEQSWIPKIFKK(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 5-17 of human TRPM4 (Accession Q8TD43). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat lung, rat heart membrane, mouse brain membrane (1:200) and mouse pancreas ms1 cell lysate (1:400).
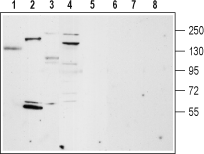 Western blot analysis of rat lung (lanes 1 and 5), rat heart membrane (lanes 2 and 6), mouse brain membrane (lanes 3 and 7) and ms1 mouse pancreas cells lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-TRPM4 Antibody (#ACC-044), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat lung (lanes 1 and 5), rat heart membrane (lanes 2 and 6), mouse brain membrane (lanes 3 and 7) and ms1 mouse pancreas cells lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-TRPM4 Antibody (#ACC-044), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-TRPM4 Antibody, preincubated with TRPM4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC044).
- Rat lung paraffin embedded section (1:100).
The mammalian melastatin-related transient receptor potential (TRPM) is a subfamily of the TRP family. The family was named after the first discovered member, melastatin (TRPM1) whose gene was identified in metastatic and benign melanomas1-3.
The TRPM family consists of eight members designated as TRPM1-8 that can be further divided into four pairs: TRPM1 and TRPM3; TRPM2 and TRPM8; TRPM4 and TRPM5; and TRPM6 and TRPM71,2.
The TRPM proteins share structural homology with other members of the TRP superfamily channels; six putative transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic N- and C-termini. However, due to their long N- and C-termini they are also named the long TRP channel family1-3.
TRPM4 and TRPM5 are the only TRP channels that are permeable to monovalent cations but not to Ca2+.
TRPM4 is expressed as at least two alternative spliced isoforms, TRPM4a and TRPM4b which consist of shorter and longer N-terminal regions, respectively. TRPM4a displays little activity, TRPM4b and TRPM5 appear to be directly activated by an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration4.
TRPM4 is expressed at relatively high levels in cardiac tissues.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
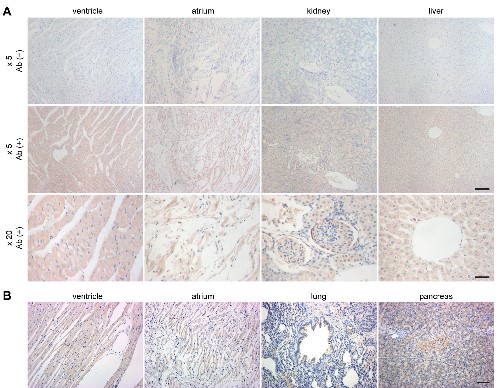
Expression of TRPM4 in various rat organs.Immunohistochemical staining of various rat organs using Anti-TRPM4 Antibody (#ACC-044) using DAB staining. TRPM4 staining (brown) is detected in rat ventricle, atrium and to a lesser extent in pancreas, kidney, liver, and lung sections.Adapted from Piao, H. et al. (2015) PLoS ONE 10, e0121703. with permission of PLoS.
