Overview
- Peptide (C)RFGAKWNYINAYDNH, corresponding to amino acid residues 942 - 956 of mouse TRPM7 (Accession Q923J1). Extracellular, 2nd loop.

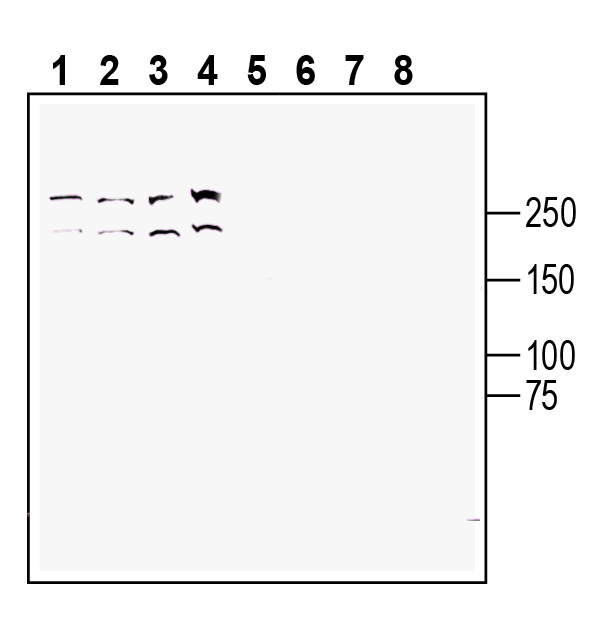 Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 5), human Raji B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 6 ), mouse WEHI B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human NK-92 natural killer cell line lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 5), human Raji B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 6 ), mouse WEHI B-cell lymphoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human NK-92 natural killer cell line lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129). Western blot analysis of rat spleen lysate:1. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat spleen lysate:1. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:200).
2. Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129).
 Expression of TRPM7 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:600), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TRPM7 immunoreactivity (green) appears in cortical neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of TRPM7 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:600), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TRPM7 immunoreactivity (green) appears in cortical neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).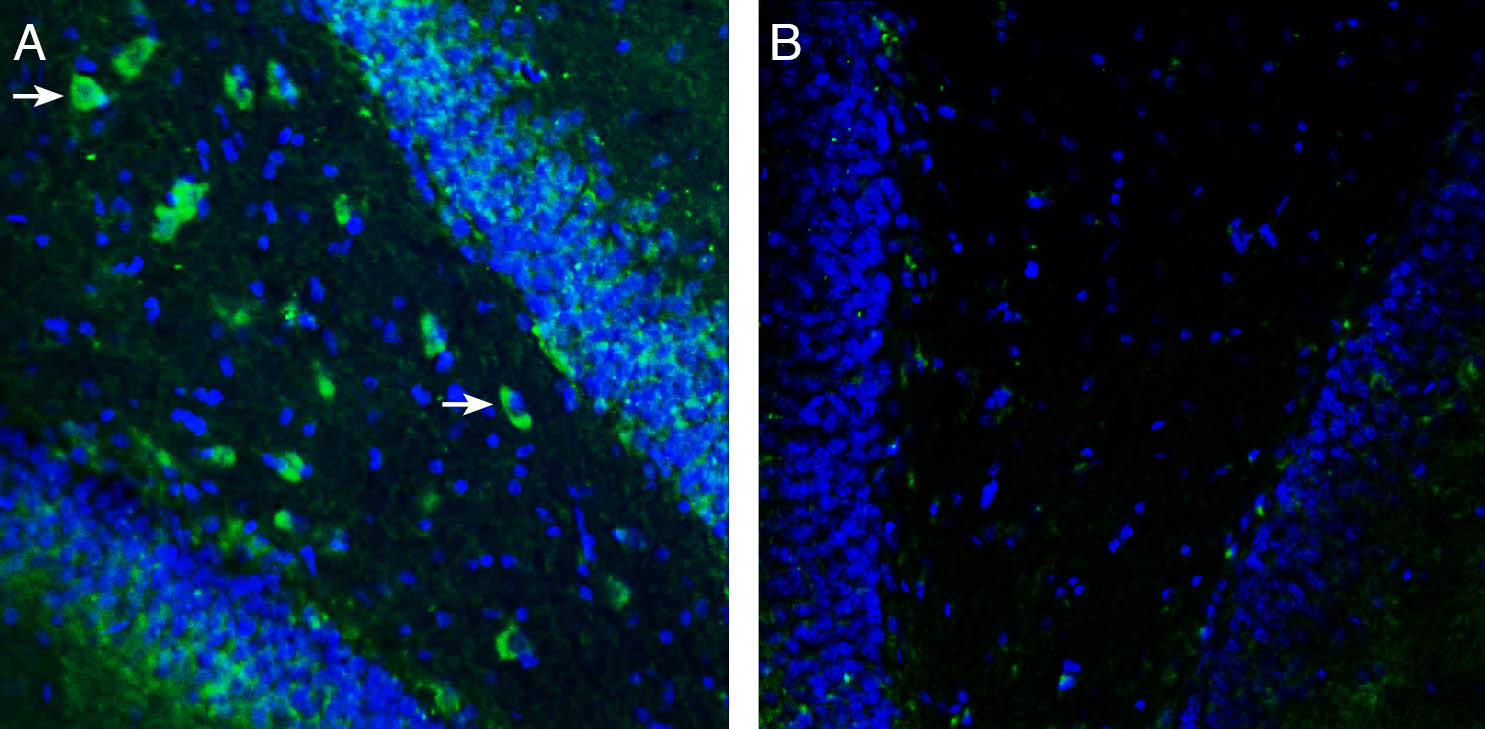 Expression of TRPM7 in rat hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:600), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus, showed TRPM7 immunoreactivity (green) in neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of TRPM7 in rat hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129), (1:600), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus, showed TRPM7 immunoreactivity (green) in neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TRPM7 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-CC129), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Montell, C. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell. 9, 229.
- Clapham, D.E. (2003) Nature 426, 517.
- Moran, M.M. et al. (2004) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 362
- Clapham, D.E. et al. (2003) Pharmacol. Rev. 55, 591.
- Harteneck, C. (2005) Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 371, 307.
- Schmitz, C. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37763.
- Aarts, M.M. et al. (2005) Neuroscientist 11, 116.
- Aarts, M.M. et al. (2005) Pflugers. Arch. 451, 243.
TRP channels are a large family (about 28 genes) of plasma membrane, non-selective cationic channels that are either specifically or ubiquitously expressed in excitable and non-excitable cells.1 The TRP channels have putative six-transmembrane domains (TM) with a pore domain between the fifth and the six TM, and all assemble as tetramers. Both the N- and the C-terminus of all TRPs are intracellular.3
According to IUPHAR the TRP family comprises of three main subfamilies on the basis of sequence homology; TRPC (canonical), TRPV (vanilloid) and TRPM (melastatin). To date, three extra subfamilies are also considered to belong to the TRP family; the TRPA, TRPML, and the TRPP.1-4
The TRPM subfamily consists of eight members, TRPM1 to TRPM8, which also can be further subdivided into four subgroups based on their sequence homology: (1)TRPM1 and TRPM3 (2) TRPM6 and TRPM7 (3) TRPM4 and TRPM5 (4) TRPM2 and TRPM8.5
TRPM7 and TRPM6 are involved in Mg2+ homeostasis and are unique among the TRP family members, possessing a functional kinase domain at their C-terminus.6,7 Although the kinase is not necessary to the function of the channel it may have a role in modulating the activation of channel 7.Recent work demonstrated that TRPM7 is a critical mediator of anoxic cell death.7,8
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-TRPM7 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-129) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize TRPM7 from rat, mouse and human samples.

