Overview
- Peptide (C)GRRASETERLLTPN, corresponding to amino acid residues 6-19 of mouse TRPLM1 (Accession Q99J21). Intracellular, N-terminus (cytoplasmic).
- Rat kidney and Human embryonic kidney 293 cells (HEK-293) lysates (1:200).
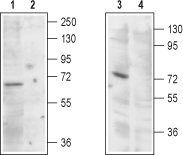 Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 2) and HEK-293 cells (lanes 3 and 4) lysates:1,3. Anti-TRPML1 (Mucolipin 1) Antibody (#ACC-081), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 2) and HEK-293 cells (lanes 3 and 4) lysates:1,3. Anti-TRPML1 (Mucolipin 1) Antibody (#ACC-081), (1:200).
2,4. Anti-TRPML1 (Mucolipin 1) Antibody, preincubated with TRPML1/Mucolipin 1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC081).
The endolysosome system takes part in important cellular functions such as membrane trafficking, protein transport, autophagy and signal transduction1. Endosomes result from endocytosis of the plasma membrane and lysosomes (which are derived from late endosomes) conatin mainly hydrolytic enzymes and generally have a low internal pH1. Like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), endolysosomes also store Ca2+ (luminal Ca2+ concentration: 0.5 mM)1,2, and similarly to Ca2+ release from the ER, Ca2+ from endolysosomes may also play an important role in various signaling events. To date such candidates include members of the TRP super-family of ion channels and the two-pore Ca2+ channels (TPCs)1,3,4.
TRPMLs, also termed mucolipins, are members of the TRP channels. In mammals, three TRPMLs are known to date (TRPML1-3 or MCOLN1-3). They are all localized to endolysosomes, although when over expressed in heterologous systems, TRPML3 is found on the plasma membrane1,5. These channels are Ca2+ permeable and display inward rectifying current properties1,5. Like all members of this family, TRPMLs have six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini (relatively short tails compared to other members). They are characterized by an exceptionally large extracellular (luminal) loop between transmembrane domains 1 and 2, and N-glycosylation sites are present in the first extracellular (luminal) loop5.
In mammals, TRPML1 is expressed in a ubiquitous manner and shows highest expression in the brain, kidney, spleen, liver and heart1,6. TRPML2 and TRPML3 are less widely expressed. Interestingly, in mouse, two splice variants exist for TRPML2. The shorter variant is more broadly expressed and is dominant over the longer variant in the thymus, spleen and kidney1,7. TRPML3 is highly detected in the thymus, lung, kidney, spleen and eye1,7,8, some epithelial cells1,9 and brain10.
Pathologies related to these channels include type IV mucolipidosis, a neurodegenetative disease characterized by retardation and retinal degeneration caused by a loss of function mutation in the gene encoding TRPML1. In contrast, a gain of function mutation in TRPML3, in mice, causes deafness, and pigmentation defects11.
