Overview
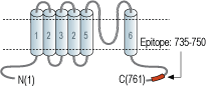
- Peptide (C)KKNPTSKPGKNSASEE, corresponding to amino acid residues 735-750 of rat TRPV2 (Accession Q9WUD2). Intracellular, C-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 2) and rat RBL basophilic leukemia lysates (lanes 3 and 4):1,3. Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 2) and rat RBL basophilic leukemia lysates (lanes 3 and 4):1,3. Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032), (1:200).
2,4. Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody, preincubated with TRPV2/VRL1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC032).
 Immunoprecipitation of rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) lysate:1. RBL lysate.
Immunoprecipitation of rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) lysate:1. RBL lysate.
2. Lysate immunoprecipitated with Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032), (7.5 µg).
3. Lysate immunoprecipitated with pre-immune rabbit serum.
The upper arrow indicates TRPV2 while the lower arrow indicates the IgG heavy chain. Western blot analysis was performed with Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody.
 Expression of TRPV2 in mouse DRGImmunohistochemical staining of TRPV2 in mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) using Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032). A. TRPV2 (green) appears in patches along the perimeter of the DRG (arrows). B. Neurons containing neurofilament 200 (red) are scattered in the DRG, also in patches (arrows). C. A merge of the two panels shows that the spatial distribution of neurofilament 200 and TRPV2 expression overlaps. However, DRGs showing robust expression of neurofilament 200 do not contain TRPV2.
Expression of TRPV2 in mouse DRGImmunohistochemical staining of TRPV2 in mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) using Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032). A. TRPV2 (green) appears in patches along the perimeter of the DRG (arrows). B. Neurons containing neurofilament 200 (red) are scattered in the DRG, also in patches (arrows). C. A merge of the two panels shows that the spatial distribution of neurofilament 200 and TRPV2 expression overlaps. However, DRGs showing robust expression of neurofilament 200 do not contain TRPV2.
- Montell, C. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9, 229.
- Clapham, D.E. (2003) Nature 426, 517.
- Moran, M.M. et al. (2004) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 362.
- Clapham, D.E. et al. (2003) Pharmacol. Rev. 55, 591.
- Gunthorpe, M.J. et al. (2002) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 183.
- Tominaga, M. and Caterina, M.J. et al. (2004) J. Neurobiol. 61, 3.
- Voets, T. et al. (2004) Nature 430, 748.
- Pedersen, S.F. et al. (2005) Cell Calcium 38, 233.
- Muraki, K. et al. (2003) Circ. Res. 93, 829.
- Shimosato, G. et al. (2005) Pain 119, 225.
- Saunders, C.I. et al. (2007) Mol. Immunol. 44, 1429.
- Caterina, M.J. et al. (1999) Nature 398, 436.
TRP channels are a large family (about 28 genes) of plasma membrane, non-selective cationic channels that are either specifically or ubiquitously expressed in excitable and non-excitable cells.1 The TRP channels have six putative transmembrane domains (TM) with a pore domain between the fifth and the sixth TM, and all assemble as tetramers. Both the N- and the C-termini of all TRPs are intracellular3.
According to IUPHAR, the TRP family is comprised of numerous subfamilies on the basis of sequence homology; TRPC, TRPM, TRPV, TRPA, TRPML, and TRPP1-4. The TRPV subfamily consists of six members, TRPV1-65.
Four members of the TRPV family have been described as thermosensitive ion channels (TRPV1 to TRPV4). Each channel exhibits distinct thermal activation thresholds ranging from noxious cold (<17°C) to noxious heat (>52°C) 6,7. Although it shares around 50% homology with TRPV1, TRPV2 is not activated by capsaicin nor by protons. It has a high temperature threshold of ~52°C and is considered to play an essential role in the perception of high-intensity noxious heat stimulation8-10. TRPV2 is also considered to be a stretch-activated channel and to play a role in skeletal and cardiac muscle degeneration and pain pathway8. The TRPV2 channel is expressed in DRG neurons, different brain regions and non-neuronal tissues such as the spleen, lung and intestine and in components of the immune system5,11,12.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-TRPV2 (VRL1) Antibody (#ACC-032) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize TRPV2 from mouse and rat samples. The antibody will not to recognize TRPV2 from human samples.
