Overview
- Peptide (C)GEFGGHDKPKITAWE, corresponding to amino acid residues 106-120 of rat vesicular GABA transporter (Accession O35458). Cytoplasmic, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human U-87 MG glyoblastoma lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human U-87 MG glyoblastoma lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody, preincubated with Vesicular GABA Transporter/VGAT Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT005).
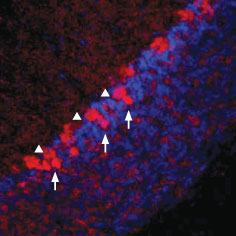 Expression of Vesicular GABA Transporter in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat frozen cerebellum sections using Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:100). VGAT staining is shown in red and dapi (blue) was used as a general cellular marker. VGAT appears in the cerebellar pinceau (arrows) and in the soma of Purkinje cells (triangles).
Expression of Vesicular GABA Transporter in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat frozen cerebellum sections using Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:100). VGAT staining is shown in red and dapi (blue) was used as a general cellular marker. VGAT appears in the cerebellar pinceau (arrows) and in the soma of Purkinje cells (triangles).
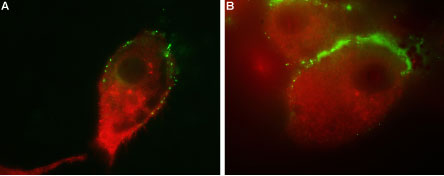 Colocalization of GluR1 and Vesicular GABA Transporter in human U-87 MG cellsImmunocytochemical staining of human glioblastoma U-87 MG. Extracellular staining of live intact cells with Guinea pig Anti-GluR1 (GluA1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-004-GP), (1:25), followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Cells were subsequently fixed, permeabilized and labeled with Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). Representative merged images of the double labeled cells are shown in A and B.
Colocalization of GluR1 and Vesicular GABA Transporter in human U-87 MG cellsImmunocytochemical staining of human glioblastoma U-87 MG. Extracellular staining of live intact cells with Guinea pig Anti-GluR1 (GluA1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-004-GP), (1:25), followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Cells were subsequently fixed, permeabilized and labeled with Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). Representative merged images of the double labeled cells are shown in A and B.
- Gasnier, B. (2004) Pflugers. Arch. 447, 756.
- McIntire, S. et al. (1997) Nature. 389, 870.
- Bedet, C. et al. (2000) J. Neurochem. 75, 1654.
- Chaudry, F. et al. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18, 9733.
- Dumoulin, A. et al. (1999) J. Cell. Sci. 112, 811.
- Takamori, S. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20, 4904.
- Mayerhofer, A. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15, 1089.
- Chessler, S. et al. (2002) Diabetes. 51, 1763.
The superfamily of amino acid transporters includes SLC32, SLC36 and SLC38 families. SLC32 has only one member, the vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter (VIAAT) or vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT)1.
VGAT is responsible for the uptake of GABA and glycine in exchange of protons, and their release from nerve terminals1.
The transporter is organized into ten membrane spanning domains, a cytosolic N-terminus and a luminal C-terminal tail2. In many regions in the brain, where it is expressed, it is found constitutively phosphorylated, although the biological significance is currently unknown3.
VGAT is expressed on synaptic vesicles of GABAergic and glycinergic neurons4-6. The transporter is also detected in the pituitary gland and in the pancreas7,8.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT) Antibody (#AGT-005) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize VGAT from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse sample:
Koga, K. et al. (2018) Mol. Pain.18,
