Overview
- Peptide (C)EDGKPLEVPEKK, corresponding to amino acid residues 45-56 of rat VGLUT2 (Accession Q9JI12). Cytoplasmic, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain lysates. Human SH-SY5Y cell line (1:400-1:1500).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-VGLUT2 Antibody (#AGC-036), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-VGLUT2 Antibody (#AGC-036), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-VGLUT2 Antibody, preincubated with VGLUT2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GC036).
- Rat brain frozen sections (1:400). Rat spinal cord (1:600).
Central nervous system neurons have traditionally been thought to express exclusively membrane transporters and/or vesicular transporters for their transmitter. Three vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUTs) have been cloned: BNPI/VGLUT1 (a brain-specific sodium dependent inorganic phosphate (Pi) transporter), and its homologs DNPI/VGLUT2 (differentiation-associated sodium-dependent Pi transporter) and VGLUT31. These transporters mediate glutamate uptake inside presynaptic vesicles and are anatomical and functional markers of glutamatergic excitatory transmission2.
BNPI/DNPI encodes a membrane protein with 6-8 putative transmembrane domains which exhibits weak similarities to a kidney Na+-dependent inorganic phosphate co-transporter3. The transporters use a membrane potential gradient set by the vesicular H+-ATPase for glutamate uptake4. VGLUT1-3 are very similar in structure and function, but are used by different neuronal populations. VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 are expressed by the cortical and subcortical neurons respectively. VGLUT3 is expressed by non-glutamatergic neurons5. VGLUT2 is expressed in the thalamus, brainstem, and deep cerebellar nuclei2. A Recent study has shown that targeted deletion of VGLUT2 in mice causes perinatal lethality and a 95% reduction in evoked glutamatergic responses in thalamic neurons, although hippocampal synapses function normally. Behavioral analysis of heterozygous VGLUT2 mice showed discrete behavioral phenotypes that suggest a deficit in thalamic processing6.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
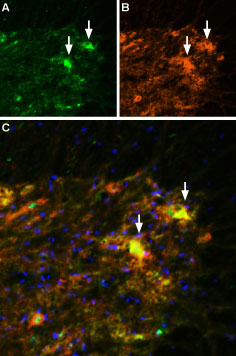 Multiplex staining of VGLUT2 and P2X7 Receptor in rat spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections using Anti-VGLUT2 Antibody (#AGC-036), (1:600) and Anti-P2X7 Receptor-ATTO Fluor-550 Antibody (#APR-004-AO), (1:100). A. VGLUT2 labeling followed by goat-anti-rabbit-Alexa-488 (green). B. The same section labeled for P2X7 receptor (orange). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates partial co-localization of Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 and P2X7 receptor in the ventral horn (arrow). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of VGLUT2 and P2X7 Receptor in rat spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections using Anti-VGLUT2 Antibody (#AGC-036), (1:600) and Anti-P2X7 Receptor-ATTO Fluor-550 Antibody (#APR-004-AO), (1:100). A. VGLUT2 labeling followed by goat-anti-rabbit-Alexa-488 (green). B. The same section labeled for P2X7 receptor (orange). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates partial co-localization of Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 and P2X7 receptor in the ventral horn (arrow). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
