Overview
- Peptide (C)KTYGQNDHTHFRND, corresponding to amino acid residues 221-234 of rat ZIP8 (Accession Q5FVQ0). 2nd extracellular loop.
 Western blot analysis of mouse kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with ZIP8/SLC39A8 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ZT008).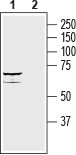 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
2. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with ZIP8/SLC39A8 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ZT008). Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line (lanes 1 and 3) and human K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line (lanes 1 and 3) and human K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with ZIP8/SLC39A8 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ZT008).
 Expression of Zinc transporter ZIP8 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. ZIP8 staining (green) appears in interneurons (arrows) adjacent to the granular layer (GL). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Zinc transporter ZIP8 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. ZIP8 staining (green) appears in interneurons (arrows) adjacent to the granular layer (GL). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Jeong, J. and Eide, D.J. (2013) Mol. Aspects Med. 34, 612.
- Aydemir, T.B. et al. (2009) J. Leukoc. Biol. 86, 337.
Zinc uptake transporter, ZIP8, belongs to the SLC39 transporter family. ZIP transporters are responsible for zinc transport into the cytoplasm across cellular membranes, either influx from the extracellular space or efflux from intracellular organelles. Regulation and maintenance of proper concentration and distribution of cellular zinc nutrient by ZIP transporters are essential to the function, metabolism, growth, proliferation and survival of cells1,2.
ZIP structure contains eight predicted transmembrane (TM) domains while the N- and C-termini are extracellular. A long loop region is present between TM3 and TM4 domains, harboring a histidine-rich region. TM4 and TM5 domains are amphipathic and are thought to form a cavity through which metals are transported1.
ZIP8 protein is encoded by the SLC39A8 gene and is highly expressed in T cells. ZIP8 also plays an important role at the onset of inflammation2.
Zinc deficiency can cause growth retardation, cognitive impairment, metabolic disorders, infertility, dysfunction of the immune system, abnormalities in T-cells, natural killer cells and monocytes, and reduction in antibody formation1,2. Studies exploring knockdown of ZIP8 protein show a reduction of cellular zinc content, impaired mitochondrial function in response to TNF-α and increased cell death2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-ZIP8 (SLC39A8) (extracellular) Antibody (#AZT-008) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat Zinc transporter ZIP8. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and indirect live cell flow cytometry. It has been designed to recognize ZIP8 from human, rat, and mouse samples.

