Overview
- Peptide (C)ELVPSARAELQSSPLVN corresponding to amino acid residues 2-18 of mouse δ-Opioid receptor (Accession P32300). Extracellular, N-terminus.

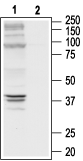 Western blot analysis of a rat cortex lysate:1. Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of a rat cortex lysate:1. Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (1:200).
2. Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with δ-Opioid Receptor/OPRD1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-OR014).
 Expression of δ opioid receptor (DOR-1) in rat spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of rat spinal cord frozen section using Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (1:100), followed by goat-anti-rabbit AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Staining is present in neuronal cell bodies (white arrows). Hoechst 33342 is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of δ opioid receptor (DOR-1) in rat spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of rat spinal cord frozen section using Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (1:100), followed by goat-anti-rabbit AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Staining is present in neuronal cell bodies (white arrows). Hoechst 33342 is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Rat neonatal drenomedullary chromaffin cells (AMCs) (Salman, S. et al. (2013) J. Physiol. 591, 515.).
- Pan, L. et al. (2005) Neuroscience 133, 209.
- http://www.iuphar-db.org/DATABASE/FamilyIntroductionForward?familyId=50
- Matthes, H.W. et al. (1998) J. Neurosci. 18, 7285.
- Di Chiara, G. and North, R.A. (1992) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 13, 185.
- Vaught, J.L. et al. (1982) Life Sci. 30, 1443.
Endogenous opiates such as endorphins, endomorphins, and enkephalins, as well as opiate drugs (including morphine) exert their effects by binding to opioid receptors. Three "classic" types of opioid receptors have been identified: mu (µ)-opioid (MOP) receptor, delta (δ)-opioid (DOP) receptor, and kappa (κ)-opioid (KOP) receptor.1 Recently, the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) peptide (NOP) receptor was also described. Despite its significant sequence homology, its pharmacological profile differs greatly from those of the classic µ, δ, and κ receptors.2
The opioid receptors belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily whose members share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus, and a third intracellular loop important for binding G proteins.1
All three classic opioid receptors mediate opioid-induced analgesia. Supraspinal analgesia is mainly mediated by the µ-opioid receptor, whereas µ-, δ-, and κ-receptors participate in the control of pain at the spinal level.3 The opioid receptors also mediate the mood-altering properties of opioids.4 Cross-talk between µ- and δ- opioid receptors was demonstrated when subeffective doses of d-opioid receptors agonists modulated m-mediated analgesia.5
The δ receptors are discretely distributed in the central nervous system (CNS), with a prominent gradient of receptor density from high levels in forebrain structures to relatively low levels in most hindbrain regions.2
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope and can potentially detect the receptor in living cells. The antibody is designed to recognize DOR-1 from mouse and rat samples. It will not recognize DOR-1 from human samples.
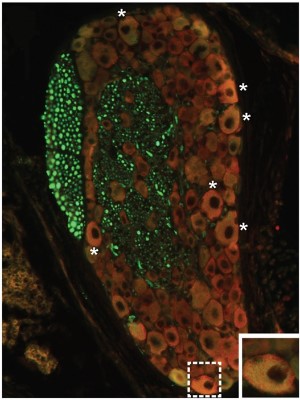
Expression of DOR-1 in mouse DRGs.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse DRG sections using Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014). DOR-1 expression (red) is expressed in DRGs and co-localizes with NF200 (green). Adapted from Reed-Geaghan, E.G. et al. (2016) J. Neurosci. 36, 4362. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
Applications
Citations
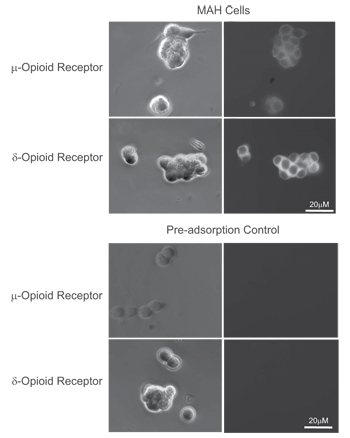 Expression of μ- and δ-opioid receptors in immortalized rat chromaffin (MAH) cells.Immunocytochemical staining of immortalized rat chromaffin (MAH) cells. A, C. Phase contrast image of MAH cells. B, D. Staining of cells with Anti-μ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-011), (B) and Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (D). E, G. Phase contrast image of MAH cells. F, H. Anti-μ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1) (extracellular) Antibody (F) and Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody were incubated prior to incubation with cells.
Expression of μ- and δ-opioid receptors in immortalized rat chromaffin (MAH) cells.Immunocytochemical staining of immortalized rat chromaffin (MAH) cells. A, C. Phase contrast image of MAH cells. B, D. Staining of cells with Anti-μ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-011), (B) and Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AOR-014), (D). E, G. Phase contrast image of MAH cells. F, H. Anti-μ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1) (extracellular) Antibody (F) and Anti-δ-Opioid Receptor (OPRD1) (extracellular) Antibody were incubated prior to incubation with cells.
Adapted from Salman, S. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.
- Rat brain sections (1:1000).
Reyes, B.A. et al. (2017) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 1007. - Mouse DRG sections (1:500).
Reed-Geaghan, E.G. et al. (2016) J. Neurosci. 36, 4362.
- Rat immortalized chromaffin (MAH) cells.
Salman, S. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 307, C266. - Rat neonatal adrenomedullary chromaffin cells (AMCs).
Salman, S. et al. (2013) J. Physiol. 591, 515.

