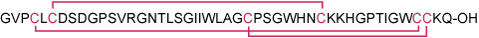Overview
Cat #:
STA-700
Alternative Name Neurotoxin 2, Toxin ATX-II, As2, Anemonia viridis toxin 2, Av2, Delta-actitoxin-Avd1c 2
Lyophilized Powder yes
Origin Synthetic peptide
MW: 4935 Da
Purity: >98% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 10-100 nM.
Sequence GVPCLCDSDGPSVRGNTLSGIIWLAGCPSGWHNCKKHGPTIGWCCKQ.
Modifications Disulfide bonds between Cys4-Cys44, Cys6-Cys34 and Cys27-Cys45.
Molecular formula C213H323N63O61S6.
CAS No.: 60748-45-0
Activity ATX-II potently modulates voltage-gated Na+ channel gating kinetics by delaying its inactivation and prolonging the action potential of excitable membranes. ATX-II has been used as a powerful activator of TTX-sensitive and insensitive Na+ channels in various excitable tissue and cell types1-9.
References-Activity
- Romey, G. et al. (1976) Proc. Natl. Acad. U.S.A. 73, 4055.
- Tesseraux, I. et al. (1987) Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 336, 232.
- Nishio, M. et al. (1991) Br. J. Pharmacol. 104, 504.
- Cannon, S.C. and Corey, D.P. (1993) J. Physiol. 466, 501.
- Hoey, A. et al. (1994) Pharmacol. Toxicol. 75, 356.
- Chahine, M. et al. (1996) J. Membr. Biol. 152, 39.
- Fletcher, J.E. et al. (1999) Anesthisiology 90, 1294.
- Brand, S. et al. (2000) Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 2387.
- Ravens, U. (1976) Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 73.
Accession number
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Any aqueous buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to four weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
 Alomone Labs ATX-II enhances hNaV1.5 currents in stably transfected HEK cells.hNaV1.5 currents were elicited by a 50 ms voltage step from the holding potential of -100 mV to -20 mV, applied every 20 sec, using whole-cell voltage clamp technique (bath solution contains TEA and pipette solution contains CsF). A. Time course, showing the effect of 0.05 nM, 0.5 nM, 5 nM and 50 nM ATX-II (#STA-700) on the current area, indicating a dose-dependent slowing of the hNaV1.5 inactivation. B. Superimposed traces of hNaV1.5 currents under control conditions and after 4-6 min perfusion with 0.05 nM, 0.5 nM, 5 nM and 50 nM ATX-II, as indicated.
Alomone Labs ATX-II enhances hNaV1.5 currents in stably transfected HEK cells.hNaV1.5 currents were elicited by a 50 ms voltage step from the holding potential of -100 mV to -20 mV, applied every 20 sec, using whole-cell voltage clamp technique (bath solution contains TEA and pipette solution contains CsF). A. Time course, showing the effect of 0.05 nM, 0.5 nM, 5 nM and 50 nM ATX-II (#STA-700) on the current area, indicating a dose-dependent slowing of the hNaV1.5 inactivation. B. Superimposed traces of hNaV1.5 currents under control conditions and after 4-6 min perfusion with 0.05 nM, 0.5 nM, 5 nM and 50 nM ATX-II, as indicated.
References - Scientific background
- Romey, G. et al. (1976) Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 4055.
- Tesseraux, I. et al. (1987) Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 336, 232.
- Nishio, M. et al. (1991) Br. J. Pharmacol. 104, 504.
- Cannon, S.C. and Corey D.P. (1993) J. Physiol. 466, 501.
- Hoey, A. et al. (1994) Pharmacol. Toxicol. 75, 356.
- Chahine, M. et al. (1996) J. Membr. Biol. 152, 39.
- Fletcher, J.E. et al. (1999) Anesthesiology 90, 1294.
- Brand, S. et al. (2000) Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 2387.
- Ravens, U. (1976) Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 73.
Scientific background
ATX-II is a 47 amino acid peptidyl toxin, originally isolated from Anemonia sulcata sea anemone venom. It is a potent neurotoxin, which modulates voltage-gated Na+ channel gating kinetics by delaying its inactivation and prolonging the action potential of excitable membranes.
ATX-II has been used as a powerful activator of TTX-sensitive and -insensitive Na+ channels in various excitable tissue and cell types (at concentration range of 10-100 nM).1-9
Target Various NaV channels
Peptide Content: 100%
Lyophilized Powder
ATX-II (#STA-700) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.
Image & Title 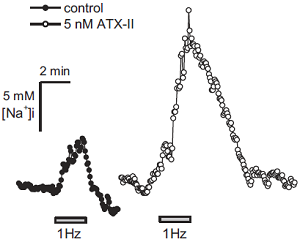
Effects of ATX-II on rabbit cardiomyocytes.Electrical stimulation-induced changes in [Na+]i in the absence (control) and presence of 5 nM ATX-II (#STA-700).Adapted from Kornyeyev, D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, H426. with permission of The American Physiological Society.

Effects of ATX-II on rabbit cardiomyocytes.Electrical stimulation-induced changes in [Na+]i in the absence (control) and presence of 5 nM ATX-II (#STA-700).Adapted from Kornyeyev, D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, H426. with permission of The American Physiological Society.
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 15/07/2024
Applications
Citations
Citations
Product citations
- Cao, Z. et al. (2018) Pharmacology 102, 253.
- Hou, J.W. et al. (2018) Br. J. Pharmacol. 175, 4325.
- Gilchrist, J. and Basmans, F. (2018) J. Physiol. 596, 1863.
- Koleske, M. et al. (2018) J. Gen. Physiol. 150, 991.
- Wei, X.H. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7, 981.
- Hampl, M. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 25974.
- Kornyeyev, D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, H426.
- Baczko, I. et al. (2014) Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 92.
- Elies, J. et al. (2014) J. Biol. Chem. 289, 16421.
- Viatchenko-Karpinski, S. et al. (2014) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 76, 247.
- Bant, J.S. et al. (2013) J. Neurosci. 33, 4976.
- Blardinelli, L. et al. (2013) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 344, 23.