Overview
- Horne, A.L. et al. (1992) Br. J. Pharmacol. 107, 732.
- Seutin, V. and Johnson S.W. (1999) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20, 268.
 Alomone Labs (-)-Bicuculline methochloride inhibits GABA(A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of GABA(A) α1/β2 currents, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 1 µM γ-Aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and reversibly inhibited by 10 µM (-)-Bicuculline methochloride (#B-137), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -60 mV.
Alomone Labs (-)-Bicuculline methochloride inhibits GABA(A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of GABA(A) α1/β2 currents, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 1 µM γ-Aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and reversibly inhibited by 10 µM (-)-Bicuculline methochloride (#B-137), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -60 mV.
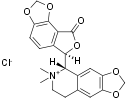
(-)-Bicuculline methochloride is a synthetic compound that acts as water soluble GABA(A) receptor antagonist. The compound is a quaternary salt of bicuculline (BIC), a competitive antagonist of the GABA(A) receptors. (-)-Bicuculline methochloride is more stable at physiological pH and more soluble in aqueous solutions than bicuculline. The compound was shown to affect other neurotransmitter systems such as the cholinergic system1.
GABA(A) receptors are members of the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. They mediate GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) action, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, through the central nervous system (CNS). They play an important role in inhibiting cell excitation in the CNS. They are considered to be a major target of antiseizure drugs2,3.