Overview
- Clozel, M. et al. (1994) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 228.
- Iglarz, M. et al. (2014) Life Sci. 118, 333.
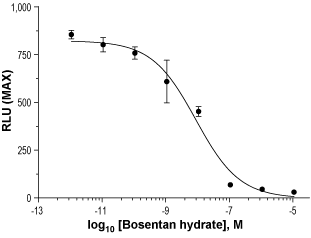 Alomone Labs Bosentan hydrate inhibits ET-A receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization in CHO cells.Dose-response curve of Bosentan hydrate (#B-170) inhibition of ET-A receptor-mediated, endothelin-1-evoked Ca2+ mobilization. IC50 was determined at 8.18 nM. Cells were loaded with Calcium 6 dye, incubated with Bosentan hydrate, and stimulated with 15 nM endothelin-1 (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
Alomone Labs Bosentan hydrate inhibits ET-A receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization in CHO cells.Dose-response curve of Bosentan hydrate (#B-170) inhibition of ET-A receptor-mediated, endothelin-1-evoked Ca2+ mobilization. IC50 was determined at 8.18 nM. Cells were loaded with Calcium 6 dye, incubated with Bosentan hydrate, and stimulated with 15 nM endothelin-1 (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
Bosentan hydrate (Ro 47-0203) is a synthetic nonpeptide compound that acts as an antagonist of endothelin A (ET-A) and endothelin B (ET-B) receptors. Bosentan hydrate is obtained by structural optimization of Ro 46-2005, a less potent ET-A/ET-B antagonist that is orally bioavailable and active in vivo. Bosentan hydrate competitively inhibits the specific binding of radioligand endothelin-1 to ET-A receptors in human smooth muscle cells with Ki value of 4.7 nM, and to ET-B receptors in human placenta with a Ki of 95 nM1. Bosentan may be a useful drug in the management of clinical disorders associated with vasoconstriction1,2.
ET-A receptors are predominantly detected in peripheral tissues, especially in vascular smooth muscle tissues where they mediate vasoconstriction. They are also expressed in several regions of the brain. ET-B receptors play an important role in regulating renal function and blood pressure and are expressed in sensory nerves. They are mainly present in medium- and large-sized cell bodies of human trigeminal ganglia. The ET-A receptor has high affinity for endothelin-1 and endothelin-2 and relatively low affinity for endothelin-3, while the ET-B receptor has high affinity for all endothelin isopeptides3,4.

