Overview
- Satow, A. et al. (2008) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326, 577.
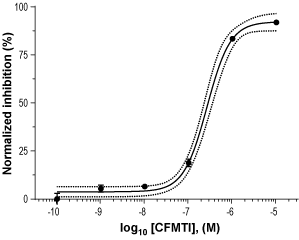 Alomone Labs CFMTI inhibits mGluR1 mediated Ca2+ mobilization in U2OS cells.Dose-response of normalized inhibition of human mGluR1 mediated, L-glutamate evoked Ca2+ mobilization by CFMTI (#C-365), showing complete inhibition at 10 µM. hmGluR1-expressing cells were loaded with Ca2+-sensitive dye, incubated with different concentrations of CFMTI, and stimulated by 15 µM L-glutamate (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following stimulation were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
Alomone Labs CFMTI inhibits mGluR1 mediated Ca2+ mobilization in U2OS cells.Dose-response of normalized inhibition of human mGluR1 mediated, L-glutamate evoked Ca2+ mobilization by CFMTI (#C-365), showing complete inhibition at 10 µM. hmGluR1-expressing cells were loaded with Ca2+-sensitive dye, incubated with different concentrations of CFMTI, and stimulated by 15 µM L-glutamate (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following stimulation were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
- Suzuki, G. et al. (2007) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 321, 1144.
- Satow, A. et al. (2008) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326, 577.
- Eom, H.S. et al. (2016) PLoS One 11, e0147538.
CFMTI is a negative allosteric modulator of mGluR1 receptors with IC50 values of 2.6 and 2.3 nM for human and rat mGluR1 expressed in CHO cells, respectively. CFMTI demonstrates high potency and selectivity for the receptor both in vitro and in vivo after oral administration and shows very low potency for other mGluR subtypes1,2.
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) that play an important role in synaptic plasticity and other neuro-physiological and pathological processes including a major role in central sensitization and neuropathic pain. Type 1 mGluRs are mainly expressed on post-synaptic neurons and are known to affect the fate of neuronal progenitor cells and neural stem cells and the formation of the hippocampus3.
CFMTI (#C-365) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

