Overview
|
Cat #:
C-390
Purity: >99%
CAS No.: 111205-55-1
MW: 309.36
Form: Lyophilized
CGS 20625 (#C-390) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.
MW: 309.36
For research purposes only, not for human use
Applications
Specifications
Properties
Technical Specifications
MW 309.36
Purity >99%
Molecular formula C18H19N3O2.
CAS No. 111205-55-1
Source Synthetic
PubChem CID 163844
Chemical name 5,6,7,8,9,10-Hexahydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)cyclohepta[b]pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridin-3(2H)-one.
Biological Activity
Target GABA(A) receptors
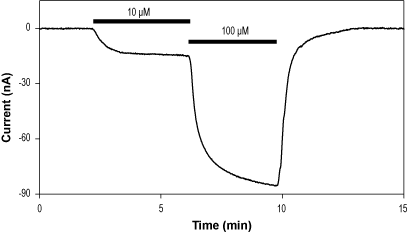
Effective concentration 1-100 µM.
Activity CGS 20625 acts as a partial agonist at GABA(A) receptors (EC50 = 11.2-23.7 µM)1. It is a potent and selective non-benzodiazepine ligand at the central benzodiazepine receptor (IC50 = 1.3 nM), with anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects in vivo2.
References
- Khom, S. et al. (2006) Mol. Pharmacol. 69, 640.
- Williams, M. et al. (1989) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248, 89.
Solubility and Storage
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at +4°C.
Solubility Soluble in DMSO and ethanol. Centrifuge before use (10000 x g, 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to three months at -20°C.
Scientific Background
References
Scientific background
CGS 20625 is a synthetic compound that acts as a potent and selective partial agonist of GABA(A) receptors.
CGS 20625 is a pyrazolopyridine compound that possesses anxiolytic and anticonvulsant characteristics. It binds to a specific recognition site on GABAA receptors containing α1, α2, α3, and α5 subunits1-3.
GABA(A) receptors are members of the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. They mediate GABA actions, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, throughout the central nervous system where it plays an important role in inhibiting cell excitation. GABA(A) receptors are a major target for antiseizure drugs4.
References
- Bennett, D.A. (1987) Physiol. Behav. 41, 241.
- Williams, M. et al. (1989) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248, 89.
- Atack, J.R. (2003) Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2, 213.
- Pomara, N. et al. (2015) Prog Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 56, 35.
Last Update: 08/01/2025