Overview
- Mullasseril, P. et al. (2010) Nat. Commun. 1, 90.
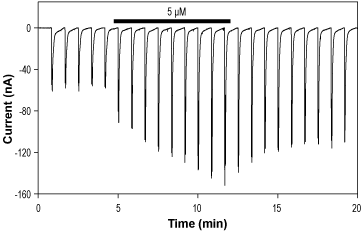 Alomone Labs CIQ potentiates NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of NR1/NR2C currents, elicited by transient stimulations with 100 µM glutamate + 40 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV, and significantly enhanced by 5 µM CIQ (#C-275).
Alomone Labs CIQ potentiates NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of NR1/NR2C currents, elicited by transient stimulations with 100 µM glutamate + 40 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV, and significantly enhanced by 5 µM CIQ (#C-275).
- Mullasseril, P. et al. (2010) Nat. Commun. 1, 90.
- Suryavanshi, P.S. et al. (2014) Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 799.
- Black, S.A. et al. (2014) Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2, 45.
CIQ is a positive allosteric potentiator selective for NR2C- and NR2D-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The compound does not potentiate other NMDA receptor subtypes or AMPA and kainate receptors. The activity of CIQ depends on a single residue in the M1 region of the receptor1,2. CIQ demonstrates potentiating EC50 values of 2.7 and 2.8 μM for NR2C- and NR2D-containing receptors, respectively1.
NMDA receptors are tetrameric entities composed of two obligatory GluN1 and two GluN2 subunits. They play important roles in numerous cellular processes and brain functions such as synaptic plasticity, addiction, and stroke. NMDA receptors also mediate physiological functions such as learning and memory formation. They are also involved in many neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease2,3.
CIQ (#C-275) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

