Overview
- Lazaro, J.T. et al. (2002) Neuropharmacology 42, 143.
- Welch, N.C. et al. (2008) Neuropharmacology 55, 1165.
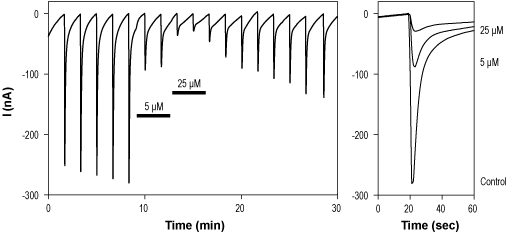 Alomone Labs CP 465022 hydrochloride inhibits GluA1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of reversible inhibition by 5 μM and 25 μM CP 465022 hydrochloride (#C-335) of glutamate-activated current (100 μM, every 100 s, at holding potential -80 mV). B. Superimposed current traces of control and inhibited currents (as indicated), taken from A.
Alomone Labs CP 465022 hydrochloride inhibits GluA1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of reversible inhibition by 5 μM and 25 μM CP 465022 hydrochloride (#C-335) of glutamate-activated current (100 μM, every 100 s, at holding potential -80 mV). B. Superimposed current traces of control and inhibited currents (as indicated), taken from A.
- Zhang, W. et al. (2006) Biophys. J. 91, 1336.
- Lazaro, J.T. et al. (2002) Neuropharmacology 42, 143.
- Welch, N.C. et al. (2008) Neuropharmacology 55, 1165.
CP 465022 hydrochloride is a selective, non-competitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor and a modulator of the voltage-gated sodium NaV1.6 channel. It has an IC50 value of 25 nM for AMPA mediated currents in rat cortical neurons and in human neuronal hNT cell lines, an IC50 of 15 nM can be observed. The inhibitory effect of CP develops slowly. The reversal of its inhibition is also slow upon compound washout, suggesting a slow rate of interaction between CP and the AMPA receptor. This may also be attributed to CP’s high lypophilicity and protein binding. CP reduces the efficacy of kainate activation of AMPA receptors at any kainate concentration, indicating that it binds to a site other than the agonist site. Inhibition of the AMPA receptor by CP is neither use-dependent nor voltage-dependent1,2. CP significantly inhibits the persistent inward Na+ current of the NaV1.6 channel in a dose-dependent manner3. This requires caution when ascribing actions to the AMPA receptor based on CP.
CP 465022 hydrochloride (#C-335) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

