Overview
- Suzuki, M. et al. (1992 ) Br. J. Pharmacol. 107, 134.
- Demaurex, N. et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 2318.
- Suzuki, M. et al. (1992 ) Br. J. Pharmacol. 107, 134.
- Demaurex, N. et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 2318.
- Zhang, P. et al. (1998) Nature 392, 835.
- Xu, C. et al. (2002) J. Mol. Biol. 316, 201.
- Moncoq, K. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 9748.
Cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) is a toxic fungal secondary metabolite. Chemically, it is an indole tetrameric acid. CPA was originally isolated from Penicillium cyclopium and subsequently from other P. cyclopium, Penicillium griseofulvum, Penicillium camembertii, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus versicolor.
CPA is a highly potent, selective and reversible inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+-ATPase pump (SERCA). This Ca2+ pump is an integral membrane protein of 994 amino acids that consists of three cytoplasmic domains containing the ATP binding site and ten transmembrane helices containing the two Ca2+ binding sites.1,2
The interchange of Ca2+ between the cell cytosol and the ER lumen by SERCA is a central process in intracellular signaling. Moreover, this process has a critical role in the muscle contraction-relaxation cycle, in which the recovery phase relies on transport of calcium into the ER by the action of the SERCA. Inhibition of this pump leads to the decrease of Ca2+ uptake from the cytosol to the ER lumen, thereby causing the depletion of Ca2+ store-operated and increase of cytosolic Ca2+.3-4
CPA inhibits the Ca2+ pump by blocking the Ca2+ access channel and immobilizing a subset of transmembrane helices.5
Cyclopiazonic Acid (#C-750) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active compound.
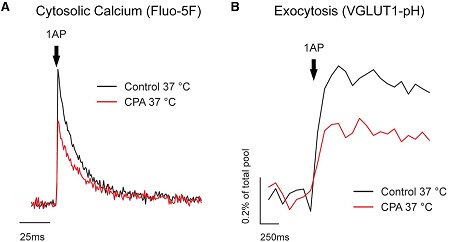
Alomone Labs Cyclopiazonic Acid blocks AP-driven Ca2+ signals and exocytosis in rat hippocampal CA1-CA3 neurons.A. Representative trace of single action potential (AP) presynaptic cytosolic Ca2+ responses measured using Fluo-5F AM before and after administration of Cyclopiazonic Acid (#C-750). B. Representative trace of single action potential (AP) presynaptic vesicular exocytosis measured using VGLUT-pH before and after Cyclopiazonic Acid treatment. Cyclopiazonic Acid blocks AP-driven Ca2+ signals and exocytosis at physiological temperatures.Adapted from de Juan-Sanz, J. et al. (2017) Neuron 93, 867. with permission of Elsevier.
Applications
Citations
- Human B-cells and HEK 293 cells.
Vierra, N.C. et al. 92017) Sci. Signal. 10, eaan2883.
- de Juan-Sanz, J. et al. (2017) Neuron 93, 867.
- Forostyak, O. et al. (2016) Stem Cell Res. 16, 622.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 308, F1135.
- Chaudhari, S. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 306, F1069.
- Grigoryan, G. and Segal, M. (2013) J. Neurophysiol. 110, 279.
- Perez, G.J. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 304, C280.
- Grigoryan, G. et al. (2012) Hippocampus 22, 1635.
- Komori, Y. et al. (2010) Cell Calcium 48, 324.
- Malkinson, G. and Spira, M.E. (2010) Cell Calcium 47, 315.
- Hegg, C.C. et al. (2009) Glia 57, 634.
- Kim, M.S. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 9733.


