Overview
- Avenet, P. et al. (1997) Neurosci. Lett. 223, 133.
- Bath, C.P. et al. (1996). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 299, 103.
 Alomone Labs Eliprodil inhibits specific binding of Ifenprodil to rat brain cortex NMDA receptors at polyamine sites.Percent inhibition of specific binding of 2 nM [3H] Ifenprodil to membranes from rat brain cerebral cortex, plotted against concentrations of Eliprodil (#E-155). Full inhibition is achieved at 3 µM.
Alomone Labs Eliprodil inhibits specific binding of Ifenprodil to rat brain cortex NMDA receptors at polyamine sites.Percent inhibition of specific binding of 2 nM [3H] Ifenprodil to membranes from rat brain cerebral cortex, plotted against concentrations of Eliprodil (#E-155). Full inhibition is achieved at 3 µM.
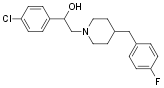
Eliprodil, also known as SL 82-0715, is a non-competitive NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor antagonist with neuroprotective properties. Eliprodil blocks the receptor through interaction with a modulatory polyamine site. The drug has also been shown to inhibit neuronal N- and P-type Ca2+ channel currents1.
NMDARs play an important role in a variety of cellular processes and brain functions including synaptic plasticity, addiction and stroke. They also mediate physiological functions such as learning and memory formation. They play a role in glutamate excitotoxicity and are involved in many neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease2.
Studies show that eliprodil has the ability to protect against ischaemia-induced neurodegeneration when the drug is administered post-occlusion and demonstrates antidepressant-like actions in preclinical tests predictive of clinical efficacy1,3.