Overview
- Suzuki, G. et al. (2009) J. Pharmacol. Sci. 110, 315.
- Fujinaga, M. et al. (2011) Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19, 102.
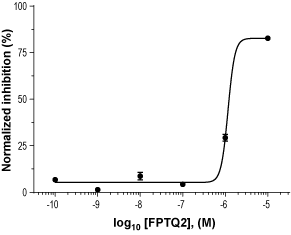 Alomone Labs FPTQ inhibits mGluR1 mediated Ca2+ mobilization in U2OS cells.Dose response of normalized inhibition of human mGluR1 mediated, L-Glutamate evoked Ca2+ mobilization by FPTQ (#F-185), showing complete inhibition at 10 µM. hmGluR1-expressing cells were loaded with Ca2+-sensitive dye, incubated with a range of concentrations of FPTQ, and stimulated by 15 µM L-Glutamate (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following stimulation were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
Alomone Labs FPTQ inhibits mGluR1 mediated Ca2+ mobilization in U2OS cells.Dose response of normalized inhibition of human mGluR1 mediated, L-Glutamate evoked Ca2+ mobilization by FPTQ (#F-185), showing complete inhibition at 10 µM. hmGluR1-expressing cells were loaded with Ca2+-sensitive dye, incubated with a range of concentrations of FPTQ, and stimulated by 15 µM L-Glutamate (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following stimulation were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
- Suzuki, G. et al. (2009) J. Pharmacol. Sci. 110, 315.
- Fujinaga, M. et al. (2011) Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19, 102.
- Satow, A. et al. (2008) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326, 577.
- Eom, H.S. et al. (2016) PLoS One 11, e0147538.
FPTQ is a synthetic compound that acts as a potent and selective allosteric antagonist of mGluR1 receptors. The compound shows very little inhibition of mGluR5 receptors. FPTQ shows high specific binding with mGluR1 receptor in the rat brain and displays IC50 values of 3.6 nM for human mGluR1 expressed in CHO cells1,2.
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) and play an important role in synaptic plasticity and other neuro-physiological and pathological processes including a major role in central sensitization and neuropathic pain. Type 1 mGluRs are mainly found in somatodendritic domains and postsynaptically regulate neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission through several intracellular second messenger systems3,4.
FPTQ (#F-185) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.