Overview
- Ling, I. et al. (2015) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 764, 497.
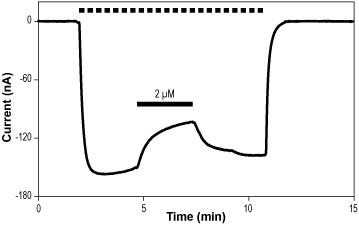 Alomone Labs GABA(A)-Compound 1b inhibits GABA(A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABA(A) α1/β2 current, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 0.1 µM γ-Aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and partially inhibited by 2 µM GABA(A)-Compound 1b (#CMG-004), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -60 mV.
Alomone Labs GABA(A)-Compound 1b inhibits GABA(A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABA(A) α1/β2 current, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 0.1 µM γ-Aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and partially inhibited by 2 µM GABA(A)-Compound 1b (#CMG-004), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -60 mV.
- Ling, I. et al. (2015) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 764, 497.
- Williams, M. et al. (1989) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248, 89.
GABA(A)-Compound 1b (8-methyl-5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-1-benzothiophen-2-yl]-1,9-dihydro-2H-[1,3]oxazolo[4,5-h][2,3]benzodiazepin-2-one) is a potent and selective antagonist of α5 containing GABA(A) receptors, displaying an IC50 value of 201 nM. On α1-4 containing receptors, the antagonist demonstrates only partial maximum inhibition1.
GABA(A)-Compound 1b is characterized as a 2,3-benzodiazepine with substantial blood-brain barrier permeability. In vivo studies reveal that 1b is devoid of sedative effects, is pro-convulsive, and enhances the performance of rats in the object recognition test.
GABA(A) receptors are members of the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. They mediate GABA action, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter throughout the central nervous system (CNS), thus play an important role in inhibiting cell excitation in the CNS.
GABA(A) receptors are considered a major target of antiseizure drugs2.
GABA(A)-Compound 1b (#CMG-004) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

