Overview
- Peptide MVSASHPEALAAPVTTVAT(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 1-19 of rat Synaptotagmin 1 (Accession P21107). Intravesicular, N- terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysates:1. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysates:1. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:400).
2. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), preincubated with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003). Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysates:1. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysates:1. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:200).
2. Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), preincubated with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003).
 Expression of Synaptotagmin-1 in rat cerebellum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-guinea pig - Alexa Fluor-594. A. Synaptotagmin-1 immunoreactivity (red) appears in the granule layer (vertical arrows) and in the molecular layer (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). M = molecular layer, P = purkinje layer, G = granule layer.
Expression of Synaptotagmin-1 in rat cerebellum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-guinea pig - Alexa Fluor-594. A. Synaptotagmin-1 immunoreactivity (red) appears in the granule layer (vertical arrows) and in the molecular layer (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). M = molecular layer, P = purkinje layer, G = granule layer.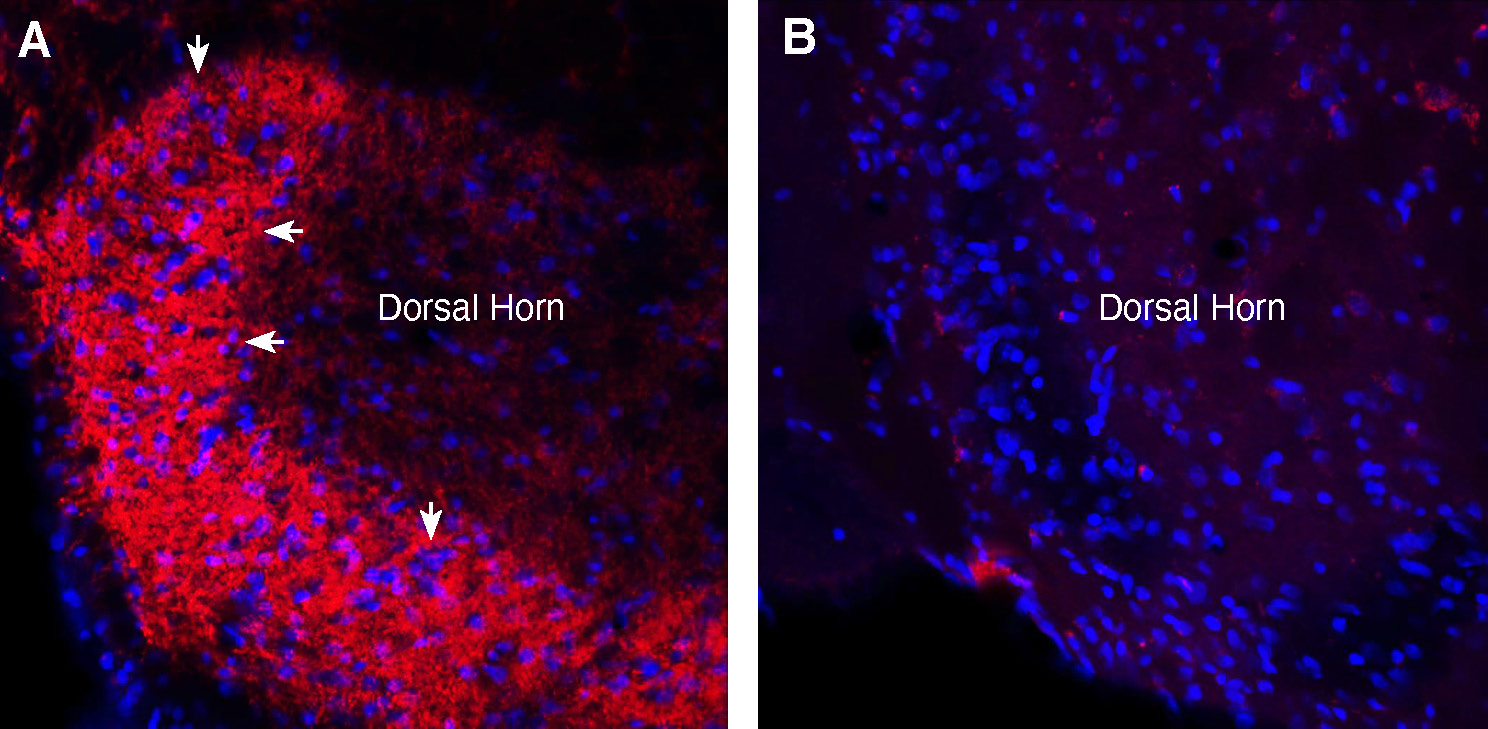 Expression of Synaptotagmin-1 in rat spinal cord.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections with Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-guinea pig - Alexa Fluor-594. A. Staining in the spinal dorsal horn region, showed Synaptotagmin-1 immunoreactivity (red) in axonal outlines in the superficial layer of the dorsal horn (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Synaptotagmin-1 in rat spinal cord.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections with Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-guinea pig - Alexa Fluor-594. A. Staining in the spinal dorsal horn region, showed Synaptotagmin-1 immunoreactivity (red) in axonal outlines in the superficial layer of the dorsal horn (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR003), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Südhof, T.C. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 7629.
- Malsam, J. et al. (2008) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 2814.
- Meir, A. et al. (1999) Physiol. Rev. 79, 1019.
Synaptotagmin 1 is a member of the Ca2+-binding synaptotagmin family of proteins that includes 16 members in vertebrates and is involved in regulated exocytosis and trafficking1,2.
Synaptotagmins are type I membrane proteins located in intracellular vesicles and consist of a short N-terminal domain located in the vesicle lumen, a transmembrane domain and a cytosolic domain containing two Ca2+ binding domains1,2.
Synaptotagmins are usually localized to distinct secretory vesicles and control their Ca2+-dependent fusion. Synaptotagmin I is predominantly expressed in neuronal cells and is an abundant constituent of synaptic vesicles1,2.
Synaptotagmin 1 has a relatively low Ca2+ affinity and is able to bind Ca2+ mostly in the vicinity of Ca2+ channels pores. Indeed, Synaptotagmin 1 has been demonstrated to directly interact with selected Ca2+ channels. Synaptotagmin 1 also binds to the t-SNARE protein Syntaxin 1 in a Ca2+-dependent manner thus forming the prototypical Ca2+-dependent fast synaptic vesicle exocytosis protein complex that also includes SNAP-25 and VAMP1,2,3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Guinea Pig Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003-GP) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Synaptotagmin-1 from mouse, rat and human samples.
The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-Synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) Antibody (#ANR-003) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation and more.
