Overview
- Koschak, A. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 2639.
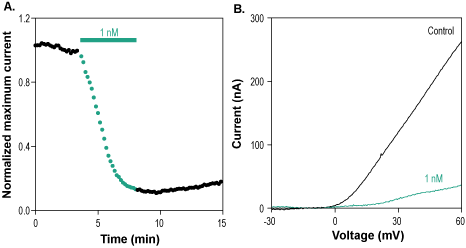 Alomone Labs Hongotoxin-1 blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Hongotoxin-1 (#STH-400) inhibition of normalized KV1.3 current at +60mV. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by 1 nM Hongotoxin-1 (green). B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current after application of control (black) and of 1 nM Hongotoxin-1 (green), taken from the recording in A.
Alomone Labs Hongotoxin-1 blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Hongotoxin-1 (#STH-400) inhibition of normalized KV1.3 current at +60mV. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by 1 nM Hongotoxin-1 (green). B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current after application of control (black) and of 1 nM Hongotoxin-1 (green), taken from the recording in A.
- Koschak, A. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 2639.
- Legros, C. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 16918.
Hongotoxin is a peptide toxin originally isolated from the scorpion Centruroides limbatus1 and was shown to block cloned and heterologously expressed (in HEK 293 cells) KV1.1, KV1.2 and KV1.3 with IC50 of 31, 170 and 86 pM respectively1. In addition, it blocks KV1.6 with lower affinity (IC50 = 6 nM).
Hongotoxin-1 action was examined by monitoring radiolabeled Rb+ efflux from KV channels-transfected HEK 293 cells. Hongotoxin-1 blocks 125I-Margtoxin (Margatoxin) binding to rat brain synaptosomes1 or 125I-Kaliotoxin binding to purified KV1.3-KcsA chimeras2. A mutated 125I-Hongotoxin-1 was used to immunoprecipitate (with specific KV antibodies) rat brain KV channels and to determine their subunit composition1.
Hongotoxin-1 (#STH-400) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.
Applications
Citations
- Meneses, D. et al. (2016) Neural Plast. 2016, 8782518.

