Overview
- Bradshaw, R.A. (1978) Ann. Rev. Biochem 47, 191.
- Huang, E.J. and Reichardt, L.F. (2001) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 677.
 Alomone Labs Recombinant human beta-NGF protein promotes survival of PC12 cells.Dose-response curve of Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245) facilitation of survival of serum-deprived PC12 cells. Cell viability was determined by the XTT method and normalized to serum-supplemented control. EC50 was calculated at 2.85 ng/ml.
Alomone Labs Recombinant human beta-NGF protein promotes survival of PC12 cells.Dose-response curve of Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245) facilitation of survival of serum-deprived PC12 cells. Cell viability was determined by the XTT method and normalized to serum-supplemented control. EC50 was calculated at 2.85 ng/ml.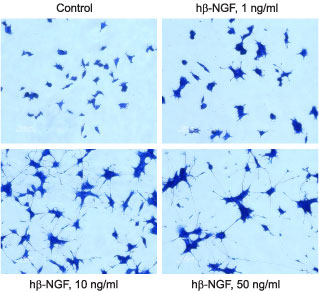 Alomone Labs Recombinant human beta-NGF protein promotes neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.Cells were grown on collagen coated 24 well plates in DMEM medium, supplemented with 6% fetal calf serum and 6% horse serum for 24 h. Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245) was added at the indicated concentrations. The culture media was changed every 2-3 days. The development of neurites over a period of 5 days was visualized by Methylene Blue staining.
Alomone Labs Recombinant human beta-NGF protein promotes neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.Cells were grown on collagen coated 24 well plates in DMEM medium, supplemented with 6% fetal calf serum and 6% horse serum for 24 h. Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245) was added at the indicated concentrations. The culture media was changed every 2-3 days. The development of neurites over a period of 5 days was visualized by Methylene Blue staining.
- Roux, P. et al. (2002) Prog. Neurobiol. 67, 203.
- Levi-Montalcini, R. (1966) Harvey Lect. 60, 217.
- Farinas, I. et al. (1998) Neuron 21, 325.
- Levi-Montalcini, R. et al. (1996) Trends Neurosci. 19, 514.
- McDonald, N.Q. et al. (1991) Nature 354, 411.
- Huang, E.J. and Reichardt, L.F. (2001) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 677.
- Freund V. and Frossard, N. (1994) Prog. Brain Res. 146, 335.
- Raychaudhuri, S.P. and Raychaudhuri, S.K. (2004) Prog. Brain Res. 146, 433.
- Kawamoto, K. and Matsuda, H. (2004) Prog. Brain. Res. 146, 369.
- Teng, K.K. and Hempstead, B.L. (2004) Cell Mol. Life Sci. 61, 35.
The neurotrophins ("neuro" means nerve and "trophe" means nutrient) are a family of soluble, basic growth factors which regulate neuronal development, maintenance, survival and death in the CNS and PNS.1 NGF, the first member of the family to be discovered, was originally purified as a factor able to support survival of sympathetic and sensory spinal neurons in culture.2 It is synthesized and secreted by sympathetic and sensory target organs and provides trophic support to neurons as they reach their final target.3
Neurotrophin secretion increases in the nervous system following injury. Schwann cells, fibroblasts, and activated mast cells normally synthesize NGF constitutively, however direct trauma and induction of cytokines combine to increase neurotrophin production in these cells after injury.4
The structural hallmark of all the neurotrophins is the characteristic arrangement of the disulfide bridges known as the cysteine knot, which has been found in other growth factors such as Platelet-derived growth factor.5 There is a 95.8% homology between the rat and mouse forms, and an 85% homology between the human and mouse.
NGF has been shown to regulate neuronal survival, development, function and plasticity.6 Recently, involvement of NGF in processes not involving neuronal cells has been shown, such as asthma,7 psoriasis8 and wound healing.9 The biological effects of NGF are mediated by two receptors: TrkA, which is specific for NGF, and p75NTR, which binds all the neurotrophins.10
Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245) is a highly pure, recombinant, and biologically active protein.
Applications
Citations
- Cohen, M.A. et al. (2016) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. in press.
- Lawn, S. et al. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 3814.
- Marques Fernandez, F. et al. (2013) Cell Death Dis. 4, 493.
- Ovejero-Benito, M.C. and Frade, J.M. (2013) PLoS ONE 5, e64890.

