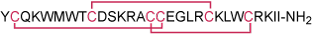Overview
Cat #:
STJ-050
Alternative Name JzTx-V, β/κ-Theraphotoxin-Cg2a, β/κ-TRTX-Cg2a, Peptide F8-15.73, Beta-theraphotoxin-Cj2a
Lyophilized Powder yes
Origin Synthetic peptide
MW: 3605.4 Da
Purity: >98% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 5-10 nM.
Sequence YCQKWMWTCDSKRACCEGLRCKLWCRKII.
Modifications Disulfide bonds between Cys2-Cys16, Cys9-Cys21, Cys15-Cys25. Ile29 - C-terminal amidation.
Molecular formula C157H243N47O37S7.
Activity Jingzhaotoxin-V inhibits TTX-resistant and TTX-sensitive Na+ channels in DRG neurons. It also highly inhibits KV4.2 and KV4.3 K+ channels and weakly inhibits KV2.1 K+ channels. It has no effect on KV1.2, KV1.3 or KV1.4 K+ channels1,2.
Accession number Q2PAY4
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Any other aqueous buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to two weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
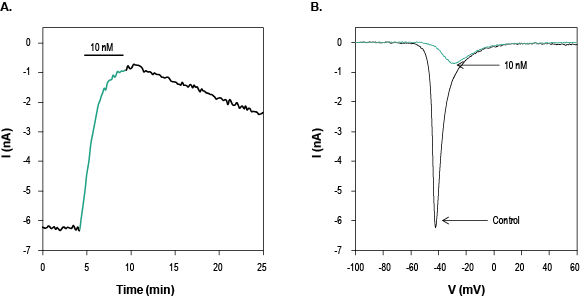 Alomone Labs Jingzhaotoxin-V inhibits NaV1.7 channels heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells.NaV1.7 currents were elicited by 30 ms voltage ramp from the holding potential of -100 mV to +60 mV, applied every 10 sec using whole-cell voltage clamp technique. A. Time course of NaV1.7 current amplitude changes before (black) and during (green) application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V (#STJ-050) indicated by the horizontal bar. B. Superimposed example current traces of NaV1.7 currents before (black) and during (green) 200 sec application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V, as indicated.
Alomone Labs Jingzhaotoxin-V inhibits NaV1.7 channels heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells.NaV1.7 currents were elicited by 30 ms voltage ramp from the holding potential of -100 mV to +60 mV, applied every 10 sec using whole-cell voltage clamp technique. A. Time course of NaV1.7 current amplitude changes before (black) and during (green) application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V (#STJ-050) indicated by the horizontal bar. B. Superimposed example current traces of NaV1.7 currents before (black) and during (green) 200 sec application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V, as indicated.
Scientific background
Jingzhaotoxin-V is a 29 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from the Chilobrachys jingzhao (Chinese earth tiger tarantula) spider1. It significantly inhibits tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) and tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) Na+ channels in adult rat DRG neurons as well as KV4.2 K+ channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes1.
It was found that Jingzhaotoxin-V alters the gating properties of Na+ channels by shifting the activation curves to the depolarizing direction and the inactivation curves to the hyperpolarizing direction1. The findings related to this peptide further reinforced the viewpoint that gating-modifier toxins can alter the voltage-dependent gating through the lipid membrane partitioning1.
Target NaV channels, KV4.2, KV4.3 channels
Peptide Content: 100%
Lyophilized Powder
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 08/01/2025
Specifications
Citations
Citations