Overview
Cat #:
L-225
Lyophilized Powder yes
Source Synthetic
MW: 380.23
Purity: >97% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 1 nM – 1 µM.
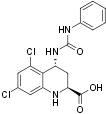
Chemical name (2S,4R)-5,7-dichloro-4-(phenylcarbamoylamino)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-2-carboxylic acid.
Molecular formula C17H15Cl2N3O3.
CAS No.: 139051-78-8
PubChem CID 121918
Activity L-689,560 is a potent and selective antagonist at the glycine site of NMDA receptors, shown to selectively inhibit [3H]-glycine binding in rat cortex membranes with IC50 of 7.4 nM, and to inhibit NMDA-evoked currents in rat cortical neurons with plC50 of 7.461.
References-Activity
- Foster, A.C. et al. (1992) Mol. Pharmacol. 41, 914.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Soluble up to 100 mM in DMSO or in ethanol. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Store at -20°C. It is recommended to prepare solutions afresh on the day of use, or aliquot stock solutions stored at -20°C to prevent repeated thawing and freezing.
Our bioassay
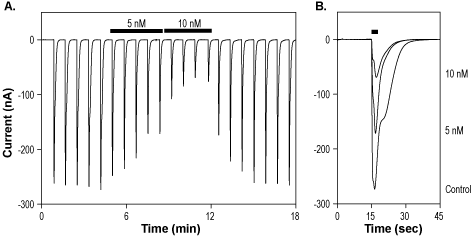 Alomone Labs L-689,560 inhibits NMDA receptor channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of NR1/NR2A currents, elicited by transient stimulations with 100 µM glutamate + 100 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -60 mV. 4 min applications of 5 nM and 10 nM L-689,560 (#L-225) reversibly inhibit current amplitude. B. Superimposed current traces from the recording shown in A, following application of control, 5 nM and 10 nM L-689,560 (as indicated). Transient stimulation is indicated by the top horizontal bar.
Alomone Labs L-689,560 inhibits NMDA receptor channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of NR1/NR2A currents, elicited by transient stimulations with 100 µM glutamate + 100 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -60 mV. 4 min applications of 5 nM and 10 nM L-689,560 (#L-225) reversibly inhibit current amplitude. B. Superimposed current traces from the recording shown in A, following application of control, 5 nM and 10 nM L-689,560 (as indicated). Transient stimulation is indicated by the top horizontal bar.
Scientific background
L-689,560 is a potent and selective antagonist at the glycine site of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. L-689,560 behaves as a full antagonist and competes with glycine for the receptors binding site1. It selectively inhibits [3H]-glycine binding in rat cortex membranes with an IC50 value of 7.4 nM1.
NMDA receptors are heterotetrameric channels formed by the assembly of two obligatory GluN1 and two GluN2/GluN3 subunits. They play an important role in a variety of cellular processes and brain functions such as, synaptic plasticity, addiction and stroke, and mediate physiological functions such as learning and memory formation and participates in glutamate excitotoxicity2.
Target NMDA receptors
Lyophilized Powder
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 08/01/2025
Specifications
Citations
Citations