Overview
- Huen, M.S. et al. (2003) Biochem. Pharmacol. 66, 125.
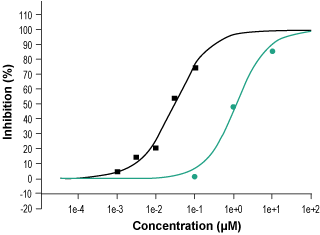 Alomone Labs Oroxylin A inhibits specific binding of Flunitrazepam to rat brain GABA(A) receptors.Percent inhibition of the specific binding of 1 nM [3H]Flunitrazepam to membranes from whole rat brain (except cerebellum) was plotted against concentrations of Oroxylin A (#O-160), (green circles) and of Diazepam (assay standard, black squares) and used to calculate IC50 and Ki values for Oroxylin A (IC50 ≈ 1.19 μM, and Ki ≈ 0.97 μM).
Alomone Labs Oroxylin A inhibits specific binding of Flunitrazepam to rat brain GABA(A) receptors.Percent inhibition of the specific binding of 1 nM [3H]Flunitrazepam to membranes from whole rat brain (except cerebellum) was plotted against concentrations of Oroxylin A (#O-160), (green circles) and of Diazepam (assay standard, black squares) and used to calculate IC50 and Ki values for Oroxylin A (IC50 ≈ 1.19 μM, and Ki ≈ 0.97 μM).
- Lee, J.Y. and Park, W. (2016) Exp. Ther. Med. 12, 151.
- Kwon, B.E. et al. (2016) PLoS One 11, 5.
- Pomara, N. et al. (2015) Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 56, 35.
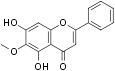
Oroxylin A, also called 6-Methoxybaicalein, is an antagonist at the benzodiazepine site of the GABA(A) receptors.
Oroxylin A is an active O-methylated flavone compound that was originally isolated from the medicinal plant Scutellaria baicalensis. Oroxylin A was shown to have multiple functions, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-thrombotic activities. In addition, it has dopamine reuptake inhibitor activity and an inhibitory effect on nuclear factor-κB activation. The compound was used to treat pulmonary infection in Korea, China, and Japan1,2.
GABA(A) receptors are members of the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. They mediate GABA action, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, through the central nervous system. The GABAA receptor is considered to be a major target of antiseizure drugs3.
Oroxylin A (#O-160) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active compound.