Overview
- Yang, C. et al. (2015) ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6, 1560.
 Alomone Labs PACA potentiates NGF-induced neurite formation in PC12 cells.Effect of 20 µM PACA (#P-340) on 2 ng/ml Native mouse NGF 2.5S protein (99%) (#N-240)-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Cells were grown on collagen-coated plates in absence (control, top-left) or in presence of 20 µM PACA (top right), 2 ng/ml NGF (bottom left) or a combination of both (bottom right). Neurite development was visualized after 8 days by Methylene Blue staining.
Alomone Labs PACA potentiates NGF-induced neurite formation in PC12 cells.Effect of 20 µM PACA (#P-340) on 2 ng/ml Native mouse NGF 2.5S protein (99%) (#N-240)-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Cells were grown on collagen-coated plates in absence (control, top-left) or in presence of 20 µM PACA (top right), 2 ng/ml NGF (bottom left) or a combination of both (bottom right). Neurite development was visualized after 8 days by Methylene Blue staining.
- Yang, C. et al. (2015) ACS Chem. Neurosci. 16, 1560.
- Gibon, J. and Barker, P.A. (2017) Neuroscientist 23, 587.
- Drubin, D.G. et al. (1985) J. Cell Biol. 101, 1799.
- Isaev, N.K. et al. (2017) Biochemistry 82, 291.
- Cirulli, F. et al. (2000) Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 123, 129.
- Heese, K. et al. (1997) Neurosci. Lett. 231, 83.
- Capsoni, S. et al. (2011) CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 10, 635.
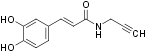
N-propargyl caffeate amide (PACA) enhances nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced neurite outgrowth, it was also shown to attenuate 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and primary rat midbrain neurons.
PACA interacts with kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) and these conjugates induce the nuclear translocation of transcription factor Nrf2 and the expression of antioxidant heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), hence PACA exhibits neuroprotective and neuritogenic activities via the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway1.
NGF belongs to a protein family called Neurotrophins, members of this family can regulate adult nervous system plasticity by promoting neuronal survival and stimulating nerve regrowth following injury. Insufficient production of neurotrophic factors is implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative disorders and hence these factors have the potential to be used as therapeutic agents2.
Nerve growth factor (NGF) regulates the microtubule-dependent extension and maintenance of axons by peripheral neurons. It also promotes microtubule assembly during neurite outgrowth3. NGF participates in the viability, development and preservation of neurons in mammalian nervous systems4,5. In addition to neuronal cells, NGF expression has been found in several types of glial cells, including olfactory cells, microglial cells, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes6. Recent studies have shown that NGF leads to neuronal apoptosis in aging, and neurodegenerative distress, and it was also shown to have a role in Alzheimer's disease7.
PACA (#P-340) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.