Overview
|
Cat #:
ANR-210-APC
Purity: >98%
CAS No.: 1262769-92-5
MW: 444.46
Form: Lyophilized
PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate (#P-280) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.
Alternative Name PD-160725 isethionate salt
MW: 444.46
For research purposes only, not for human use
Applications
Our Bioassay
Our bioassay
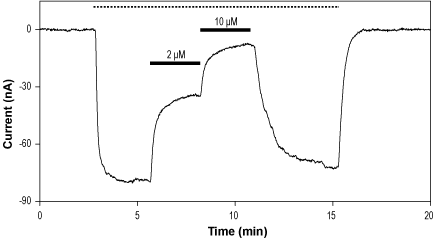 Alomone Labs PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate inhibits GluA1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of GluA1 currents, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 1 µM glutamate, and reversibly inhibited by 2 µM and 10 µM PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate (#P-280), as indicated (bars), at a holding potential of -80 mV.
Alomone Labs PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate inhibits GluA1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of GluA1 currents, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 1 µM glutamate, and reversibly inhibited by 2 µM and 10 µM PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate (#P-280), as indicated (bars), at a holding potential of -80 mV.
Specifications
Properties
Technical Specifications
MW 444.46
Purity >98%
Molecular formula C17H24N4O8S.
CAS No. 1262769-92-5
Source Synthetic
PubChem CID 71312022
Chemical name 2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid;6-methyl-7-nitro-5-(piperidin-1-ylmethyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-dione.
Biological Activity
Target AMPA receptors
Effective concentration 0.1-100 µM.
Activity PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate is an AMPA receptor antagonist.
Solubility and Storage
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Up to 20 mM in H2O (slowly, clear yellow solution). Centrifuge all products before reconstitution (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to four weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C. It is recommended to aliquot reconstituted stock solutions.
Scientific Background
References
Scientific background
PD-160725 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate is an AMPA receptor antagonist. Antagonists of AMPA receptors are good candidates for potential treatment of several neurological disorders including epilepsy, stroke and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis1,2.
The ionotropic glutamate AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are the primary receptors that mediate fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the mammalian brain. The majority of this transmission in the mammalian central nervous system is mediated by the release of glutamate from the presynaptic terminal and its binding to glutamate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane2.
References
- Niu, L. (2015) Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 5, 500.
- Guntupalli, S. et al. (2016) Neural. Plast. 2016, 3204519.
Last Update: 08/01/2025

