Overview
|
| Bioz Stars Product Rating | |
| The world's only objective ratings for scientific research products | |
| Mentions | |
| Recency | |
| View product page > | |
ProTx-I (#STP-400) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.
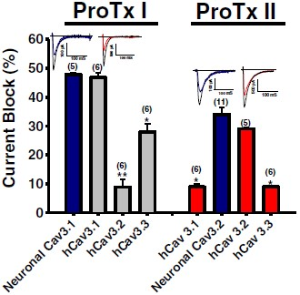
Alomone Labs ProTx-I and ProTx-II inhibit T-type CaV channels.ProTx-I (#STP-400) was applied to mouse thalamic neurons and ProTx-II (#STP-100) was tested on mouse DRGs. ProTx-I blocks native mouse CaV3.1 channel and recombinant human CaV3.1 channel currents similarly, and blocks to a lesser extent CaV3.2 and CaV3.3 channel currents. ProTx-II blocks CaV3.2 channels more potently than the other T-type currents.Adapted from Bladen, C. et al. (2014) Mol. Brain 7, 36. with permission of BioMed Central.
Applications
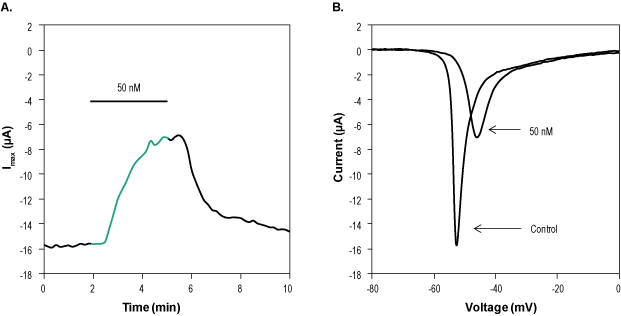 Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits NaV1.5 currents in stably transfected HEK293 cells.A. Time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) action. Current amplitudes were plotted as a function of time. Holding potential was -100 mV and currents were stimulated every 10 seconds by a voltage ramp of 50 msec from holding potential to +60 mV. 50 nM ProTx-I was perfused in the period marked by the horizontal bar (green). B. Superimposed traces of NaV1.5 currents before and during 3 min application of 50 nM ProTx-I.
Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits NaV1.5 currents in stably transfected HEK293 cells.A. Time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) action. Current amplitudes were plotted as a function of time. Holding potential was -100 mV and currents were stimulated every 10 seconds by a voltage ramp of 50 msec from holding potential to +60 mV. 50 nM ProTx-I was perfused in the period marked by the horizontal bar (green). B. Superimposed traces of NaV1.5 currents before and during 3 min application of 50 nM ProTx-I. Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits CaV3.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) inhibition of CaV3.1 maximum current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage step to -30 mV every 10 sec, and was significantly inhibited by application of 1 µM ProTx-I (top horizontal bar). B. Superimposed traces of CaV3.1 current following the application of control and of 1 µM ProTx-I (as indicated). Taken from experiment in A.
Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits CaV3.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) inhibition of CaV3.1 maximum current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage step to -30 mV every 10 sec, and was significantly inhibited by application of 1 µM ProTx-I (top horizontal bar). B. Superimposed traces of CaV3.1 current following the application of control and of 1 µM ProTx-I (as indicated). Taken from experiment in A. Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits NaV1.7 channel currents heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) inhibition of NaV1.7 channels current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage step to -10 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by application of 250 nM ProTx-I (green).
Alomone Labs ProTx-I inhibits NaV1.7 channel currents heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of ProTx-I (#STP-400) inhibition of NaV1.7 channels current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage step to -10 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by application of 250 nM ProTx-I (green).
B. Superimposed traces of NaV1.7 channel currents in the absence (control) and presence (green) of 250 nM ProTx-I (taken from the recording in A).
Citations (2)
- Bladen, C. et al. (2014) Mol. Brain 7, 36.
Specifications
Technical specifications
Biological activity
Solubility and storage
Scientific Background
Native ProTx-I has been isolated from the venom of the tarantula Thrixopelma pruriens. It was purified on the basis of its ability to reversibly inhibit the tetrodotoxin (TTX)-resistant Na channel NaV1.8. ProTx-I was also found to be an inhibitor of NaV1.5, NaV1.7 and NaV1.3 with IC50 values below 100 nM. Furthermore, ProTx-I shifts the voltage dependence activity of CaV3.1 (α1G) (IC50 ~50 nM) without affecting the voltage dependence of inactivation1,2. ProTx-I also blocks TRPA1 channel with an IC50 of 0.39 µM3.
Structurally, ProTx-I is shown to belong to the inhibitory cystine knot (ICK) family of peptidyl toxins interacting with voltage-gated ion channels.
- Middleton, R.E. et al. (2002) Biochemistry 41, 14734.
- Bosmans, F. et al. (2006) Mol. Pharmacol. 69, 419.
- Gui, J. et al. (2014) Curr. Biol. 24, 473.

