Overview
Cat #:
Q-100
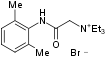
Alternative Name Lidocaine N-ethyl bromide
Lyophilized Powder yes
Source Synthetic
MW: 343.3
Purity: >99% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 1-50 mM.
Chemical name N-(2,6-Dimethylphenylcarbamoylmethyl) triethylammonium bromide.
Molecular formula C16H27N2OBr.
CAS No.: 21306-56-9
Activity QX-314 bromide is an intracellular blocker of NaV channels1-4.
References-Activity
- Llinas, R. and Yarom, Y. (1981) J. Physiol. 315, 549.
- Congar, P. et al. (1995) J. Neurophysiol. 73, 421.
- Li, D.P. et al. (2005) J. Neurophysiol. 93, 393.
- Koike-Tani, M. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25, 199.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for four years.
Solubility Water. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to two weeks at 4°C or six months at -20°C.
Protect from light. Hygroscopic.
Protect from light. Hygroscopic.
Our bioassay
 Alomone Labs QX-314 bromide inhibits native NaV channels in ND7-23 cells.Currents were elicited from a holding potential of -100 mV and test pulses of 40 ms to -10 mV were delivered every 15 sec. Superimposed traces of control currents (black) and during a bath perfusion of 2.5 mM (blue) and 25 mM (orange) QX-314 bromide (#Q-100).
Alomone Labs QX-314 bromide inhibits native NaV channels in ND7-23 cells.Currents were elicited from a holding potential of -100 mV and test pulses of 40 ms to -10 mV were delivered every 15 sec. Superimposed traces of control currents (black) and during a bath perfusion of 2.5 mM (blue) and 25 mM (orange) QX-314 bromide (#Q-100).
References - Scientific background
- Sunami, A. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 2326.
- Llinas, R. and Yarom, Y. (1981) J. Physiol. 315, 549.
- Congar, P. et al. (1995) J. Neurophysiol. 73, 421.
- Li, D.P. et al. (2005) J. Neurophysiol. 93, 393.
- Koike-Tani, M. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25, 199.
Scientific background This local anesthetic is a blocker of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. QX-314 blocks all NaV channels once exposed to the intracellular face of the channel protein. However, this compound can penetrate the cell interior once applied outside the cell. Via certain types of NaV channels, it can permeate and exert blocking activity via TTX-sensitive channels.1 Intracellular recordings from inferior olivary neurons in brain stem slice preparations demonstrated that the Na+-dependent action potential was completely blocked for approximately five minutes after impalement with a microelectrode containing 50 mM QX-314, whereas the low-threshold Ca2+ spike was still generated.2 QX-314 is widely used to block NaV channels and used as a tool in neurophysiological recordings.2-5
Target Various NaV Na+ channels
Lyophilized Powder
QX-314 bromide (#Q-100) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 12/03/2025
Applications
Citations
Citations
Product citations
- Marcoux, C.M. et al. (2016) J. Neurophysiol. 115, 530.
- Scheuss, V. and Bonhoeffer, T. (2014) Cereb. Cortex 24, 3142.
- Suvrathan, A. et al. (2013) Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 369, 20130151.
- Armogida, M. et al. (2010) Synapse 64, 161.
- Marchionni, I. et al. (2010) J. Physiol. 588, 2859.
- Sanon, N.T. et al. (2010) Epilepsia 51, 1607.
- Zhan, R.Z. et al. (2010) J. Neurophysiol. 104, 3293.
- Cohen, D. and Segal, M. (2009) J. Neurophysiol. 101, 2077.
- Drew, G.M. et al. (2009) J. Neurosci. 29, 7220.
- Hermann, J. et al. (2009) J. Neurophysiol. 101, 20.
- Marchionni, I. and Maccaferri, G. (2009) J. Physiol. 587, 5691.
- Pilpel, Y. et al. (2009) J. Physiol. 587, 787.
- Watanabe, K. et al. (2009) J. Neurophysiol. 101, 665.
- Abrahamsson, T. et al. (2008) J. Neurophysiol. 100, 2605.
- Graciotti, L. et al. (2008) Neuromuscul. Disord. 18, 220.
- Li, D.P. et al. (2008) J. Physiol. 586, 1637.
- Olijslagers, J.E. et al. (2008) Eur. J. Neurosci. 27, 2542.
- Xing, J. et al. (2008) Neuropharmacology 54, 734.
- Abrahamsson, T. et al. (2007) J. Neurophysiol. 98, 2604.
- Chen, Q. and Pan, H.L. (2007) J. Neurophysiol. 97, 3279.
- Fujiwara-Tsukamoto, Y. et al. (2007) Eur. J. Neurosci. 25, 2713.
- Singhal, S.K. et al. (2007) Neuropharmacology 52, 387.
- Zhang, H.M. et al. (2007) J. Neurophysiol. 97, 102.
- Akerman, C.J. and Cline, H.T. (2006) J. Neurosci. 26, 5117.
- Boddy, G. et al. (2006) Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 84, 589.
- Chen, Q. and Pan, H.L. (2006) Neuroscience 142, 595.
- Nuriya, M. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 786.
- Tu, B. et al. (2006) Neuroscience 143, 1085.
- Abrahamsson, T. et al. (2005) J. Physiol. 569, 737.
- Guatteo, E. et al. (2005) J. Neurophysiol. 94, 3069.
- Karst, H. and Joëls, M. (2005) J. Neurophysiol. 94, 3479.
- Karst, H. et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 19204.
- Parent, A.T. et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25, 1540.
- Bailey, S.J. et al. (2004) Neuropharmacology 46, 31.
- Drew, G.M. and Vaughan, C.W. (2004) Neuropharmacology 46, 927.
- Li, D.P. et al. (2004) J. Neurophysiol. 92, 1807.
- Maggi, L. et al. (2004) J. Physiol. 559, 863.
- Sasaki, K. et al. (2004) Mol. Pharmacol. 66, 330.
- Voronin, L.L. et al. (2004) Neuroscience 126, 45.
- Dalby, N.O. and Mody, I. (2003) J. Neurophysiol. 90, 786.
- Fujiwara-Tsukamoto, Y. et al. (2003) Neuroscience 119, 265.
- Karst, H. and Joëls, M. (2003) J. Neurophysiol. 89, 625.
- Li, D.P. et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23, 5041.
- Ogier, R. and Raggenbass, M. (2003) Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 2639.
- Strege, P.R. et al. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 285, G1111.
- Yu, Y. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 3907.
- Chuhma, N. and Ohmori, H. (2002) J. Neurophysiol. 87, 222.
- Kita, H. (2001) Neuroscience 105, 871.
- Lupica, C.R. et al. (2001) J. Neurophysiol. 86, 261.
- Mannaioni, G. et al. (2001) J. Neurosci. 21, 5925.
- Mori, M. et al. (2001) J. Physiol. 535, 115.
- Carlson, G.C. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20, 2011.
- Gasparini, S. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 9741.
- Guatteo, E. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20, 6013.
- Jensen, K. et al. (2000) Brain Res. 880, 198.
- Mothet, J.P. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 4926.
- Zaninetti, M. and Raggenbass, M. (2000) Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 3975.