Overview
- Rundfeldt, C. (1997) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 336, 243.
- Wickenden, A.D. et al. (2000) Mol. Pharmacol. 58, 591.
- Tatulian, L. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 21, 5535.
- Main, M.J. et al. (2000) Mol. Pharmacol. 58, 253.
- Brodie, M.J. et al. (2010) Neurology 75, 1817.
 Alomone Labs Retigabine enhances KCNQ2/3 (KV7.2/7.3) currents in Xenopus oocytes.A. Superimposed traces (responses to 600 ms voltage steps from -50 mV to 0 mV, holding potential -100 mV, applied every 10 sec) of KCNQ2/3 channel current responses, before (left) and during (right) application of 10 µM Retigabine (#R-100). B. Time course of current amplitude at -50 mV (holding potential -100 mV, applied every 10 sec) before, during application of 0.1 and 1 µM Retigabine (indicated by bars) and upon wash, demonstrating the current amplitude enhancement. C. I-V relations in an experiment such as in A (left before, and right, during Retigabine application). D. Voltage dependence of current increase/decrease by Retigabine.
Alomone Labs Retigabine enhances KCNQ2/3 (KV7.2/7.3) currents in Xenopus oocytes.A. Superimposed traces (responses to 600 ms voltage steps from -50 mV to 0 mV, holding potential -100 mV, applied every 10 sec) of KCNQ2/3 channel current responses, before (left) and during (right) application of 10 µM Retigabine (#R-100). B. Time course of current amplitude at -50 mV (holding potential -100 mV, applied every 10 sec) before, during application of 0.1 and 1 µM Retigabine (indicated by bars) and upon wash, demonstrating the current amplitude enhancement. C. I-V relations in an experiment such as in A (left before, and right, during Retigabine application). D. Voltage dependence of current increase/decrease by Retigabine.
The KCNQ family of voltage-gated K+ channels includes five known members: KCNQ1 to KCNQ5. Structurally, the KCNQ family belongs to the six transmembrane domain category of K+ channels. KCNQ family members can form either homomultimeric or heteromultimeric channels with different functional consequences. For example, KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 heteromultimers give rise to a much larger channel current than when either protein is expressed alone. Indeed, KCNQ2/KCNQ3 heteromultimers are believed to be the molecular correlates of the so-called M current. This current is a K+ neuronal current that is strongly inhibited by the activation of the M1 subtype of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Mutations in either KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 are associated with a form of epilepsy known as benign familial neonatal convulsions (BNFC)1-3.
Retigabine is a potent and selective KCNQ (KV7, M-) channel modulator (enhancer)4-7, which is used in the clinic to treat epilepsy8. Retigabine (0.1 to 10 µM) induced a K+ current and hyperpolarized CHO cells expressing KV7.2/3 cells5 as well as other channels in the following order: KV7.3 > KV7.2/3 > KV7.2 > KV7.46. Similar effects were seen with 10 µM retigabine in oocytes expressing the KV7.2/3 heteromeric channel7.
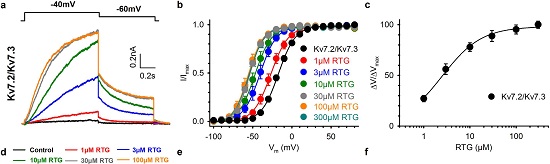
Alomone Labs Retigabine activates KCNQ2/KCNQ3 channels in HEK 293 transfected cells.A. Retigabine (#R-100) activates KCNQ2/KCNQ3 channels in a concentration-dependent manner. B. Increasing concentrations of Retigabine causes a gradual hyperpolarization shift. C. Concentration-effect curve plotted as the shift in the voltage dependence of activation normalized, as a function of the concentration of Retigabine.
Adapted from Stas, J.I. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 35080. with permission of NATURE SPRINGER.

