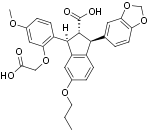
Overview
SB209670 is a nonpeptide synthetic compound that acts as a potent and specific antagonist of endothelin A (ET-A) and B (ET-B) receptors. Intravenous or intraduodenal administration of SB209670 can produce concentration-dependent inhibition of ET-1-mediated vasoconstriction in isolated vascular tissues. Studies on hypertensive rats show that SB209670 produces a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure. In a gerbil stroke model SB209670 is protective in ischemia-induced neuronal degeneration. Thus, SB209670 can be used as a useful tool in characterizing and classifying the physiological and pathophysiological roles of Endothelin receptors1.
ET-A receptors are predominantly expressed in peripheral tissues, especially in vascular smooth muscle tissues where they mediate vasoconstriction. They are also present in several different regions of the brain. ET-B receptors play an important role in regulating renal function and blood pressure and are expressed in sensory nerves. They are mainly present in medium- and large-sized cell bodies of human trigeminal ganglia.
ET-A receptor has high affinity for endothelin-1 and endothelin-2 and relatively low affinity for endothelin-3, while the ET-B receptor has high affinity equally for all endothelin isopeptides2,3.
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Biological Activity
- Ohlstein, E.H. et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 8052.
Solubility and Storage
Applications
 Alomone Labs SB209670 inhibits ETA receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization in CHO cells.Dose response curve of SB209670 (#S-205) inhibition of ET-A receptor-mediated, Endothelin-1-evoked Ca2+ mobilization. IC50 was determined at 0.91 nM. Cells were loaded with Calcium 6 dye, incubated with SB209670, and stimulated with 15 nM Endothelin-1 (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.
Alomone Labs SB209670 inhibits ETA receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization in CHO cells.Dose response curve of SB209670 (#S-205) inhibition of ET-A receptor-mediated, Endothelin-1-evoked Ca2+ mobilization. IC50 was determined at 0.91 nM. Cells were loaded with Calcium 6 dye, incubated with SB209670, and stimulated with 15 nM Endothelin-1 (EC80). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™.