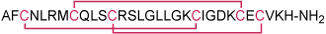Overview
- Wadsworth, J.D. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18053.
- Grissmer, S. et al. (1992) J. Gen. Physiol. 99, 63.
- Jager, H. and Grissmer, S. (1997) Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 7, 179.
 Alomone Labs Scyllatoxin inhibits rSK2 channels stably expressed in HEK293T cells.rSK2 channel currents were measured using whole cell voltage clamp in the presence of Ca2+ in the pipette solution. A voltage ramp from -120 mV to +60 mV was applied every 10 sec from a holding potential of -80 mV. A. Time course of current amplitude at 0 mV before (black) and during (green) application of 1 nM Scyllatoxin (#STS-370). B. Representative current traces at control conditions (black) and following 140 s application of 1 nM Scyllatoxin (green), taken from the experiment in A.
Alomone Labs Scyllatoxin inhibits rSK2 channels stably expressed in HEK293T cells.rSK2 channel currents were measured using whole cell voltage clamp in the presence of Ca2+ in the pipette solution. A voltage ramp from -120 mV to +60 mV was applied every 10 sec from a holding potential of -80 mV. A. Time course of current amplitude at 0 mV before (black) and during (green) application of 1 nM Scyllatoxin (#STS-370). B. Representative current traces at control conditions (black) and following 140 s application of 1 nM Scyllatoxin (green), taken from the experiment in A. Alomone Labs Scyllatoxin inhibits KCa2.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Oocyte membrane potential was held at +5 mV (in a low Cl- solution) and currents were elicited by intraoocyte CaCl2 injection. During the period marked by a green trace (30 seconds), 100 nM of Scyllatoxin (#STS-370) was applied by perfusion.
Alomone Labs Scyllatoxin inhibits KCa2.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Oocyte membrane potential was held at +5 mV (in a low Cl- solution) and currents were elicited by intraoocyte CaCl2 injection. During the period marked by a green trace (30 seconds), 100 nM of Scyllatoxin (#STS-370) was applied by perfusion.
- Chicchi, G.G. et al. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 10192.
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C. and Possani, L.D. (2004) Toxicon 43, 865.
- Auguste, P. et al. (1992) Biochemistry 31, 648.
- Wadsworth, J.D. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18053.
- Grissmer, S. et al. (1992) J. Gen. Physiol. 99, 63.
- Jager, H. and Grissmer, S. (1997) Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 7, 179.
- Auguste, P. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem., 265, 4753.
- Goh, J.W. et al. (1992) Brain Res. 591. 165.
- Pedarzani, P. et al. (2000) J. Physiol. 527, 283.
- Strøbaek, D. et al. (2000) Br. J. Pharmacol. 129, 991.
Scyllatoxin is a 31 amino acid long toxin, originally isolated from the Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus scorpion venom, and is classified as α-KTx 5.1 scorpion toxin family, having three disulfide bridges1,2.
Scyllatoxin was shown to compete with 125I-apamin binding in the brain3. Furthermore, Scyllatoxin appears to be selective for apamin-sensitive SK channels. Scyllatoxin inhibits apamin-sensitive SK channel activity in guinea-pig and rabbit hepatocytes4, SK currents in human lymphoblastoma cells5,6, and epinephrine-induced relaxation of visceral smooth muscle7.
Scyllatoxin also inhibits the apamin-sensitive after hyperpolarization that follows action potentials in skeletal muscle7 and neurons8. The SK channel-mediated after hyperpolarising current (IAHP) of dorsal vagal neurons, presuming Kca2.3 (SK3), were blocked by Scyllatoxin (20-30 nM)9. HEK 293 cell currents stably expressing hKca2.1 (hSK1) and Kca2.2 (hSK2) were blocked by Scyllatoxin with an IC50 of 80 nM and 287 pM, respectively10.
Scyllatoxin (#STS-370) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.