Overview
ShK (Stichodactyla Toxin) is a peptidyl toxin originally isolated from the nematocyst of the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus.1
ShK blocks KV1.3, KV1.1, KV1.4, and KV1.6 at subnanomolar concentrations and KV3.2 channels at 1000-fold higher concentration than that required to inhibit KV1.3 channels. It has been shown to block KV current in DRG neurons, to displace radioactive Dendrotoxin from brain synaptosomes1 and inhibit I125-Charybdotoxin binding to Jurkat T lymphocytes with an IC50 of 32 pM.2,4
Evidence also suggests that native KV currents in the central nervous system, which are predominantly carried by KV1.2 channels, are highly sensitive to this toxin.5
A fluorescently labeled synthetic ShK is used to recognize and to sort KV1.3 containing lymphocytes.4,6
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Biological Activity
- Pennington, M.W. et al. (1995) Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 46, 354.
- Beeton, C. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 9928.
- Middleton, R.E. et al. (2003) Biochemistry 42, 13698.
Solubility and Storage
Applications
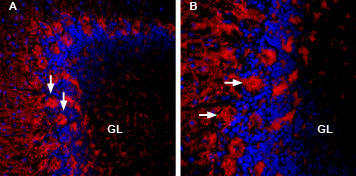 Alomone Labs Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin stains rat cerebellum.Mildly fixed rat cerebellum sections were incubated with 25 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (#STS-400-B) followed by streptavidin-Cy3 (red). Staining of Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) is seen acquired by A. 25x objective B. 40x objective. Using the 40x objective, grains scattered over the soma of purkinje cells can be seen (horizontal arrows). DAPI (blue) is used as the counterstain.
Alomone Labs Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin stains rat cerebellum.Mildly fixed rat cerebellum sections were incubated with 25 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (#STS-400-B) followed by streptavidin-Cy3 (red). Staining of Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) is seen acquired by A. 25x objective B. 40x objective. Using the 40x objective, grains scattered over the soma of purkinje cells can be seen (horizontal arrows). DAPI (blue) is used as the counterstain. Indirect flow cytometry of Stichodactyla toxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
Indirect flow cytometry of Stichodactyla toxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
___ PC-12 cells + 100 nM ShK (Stichodactyla Toxin) (#STS-400) + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.
___ PC-12 cells + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.
___ PC-12 cells + 100 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (#STS-400-B) + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.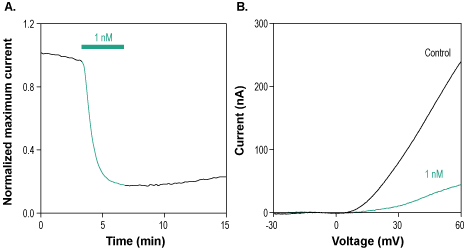 Alomone Labs Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (#STS-400-B) inhibition of KV1.3 current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by 1 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (green). B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current following application of control (black) and of 1 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (green), taken from the recording in A.
Alomone Labs Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (#STS-400-B) inhibition of KV1.3 current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV, current was elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec, and significantly inhibited by 1 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (green). B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current following application of control (black) and of 1 nM Stichodactyla Toxin-Biotin (green), taken from the recording in A.

