Overview
- Nishio, H. et al. (1996) Gen. Pharmacol. 27, 779.
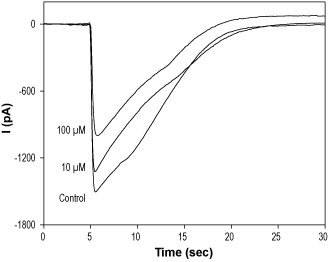 Alomone Labs Talipexole dihydrochloride (B-HT 920) blocks 5-HT3A receptors expressed in HEK 293T cells.Currents were elicited by 10 µM 5-HT, delivered every 3 minutes. Talipexole dihydrochloride (#B-140) was applied 30 seconds before stimulation at 10 and 100 µM, as indicated and inhibited the 5-HT induced current in a dose-dependent and reversible manner.
Alomone Labs Talipexole dihydrochloride (B-HT 920) blocks 5-HT3A receptors expressed in HEK 293T cells.Currents were elicited by 10 µM 5-HT, delivered every 3 minutes. Talipexole dihydrochloride (#B-140) was applied 30 seconds before stimulation at 10 and 100 µM, as indicated and inhibited the 5-HT induced current in a dose-dependent and reversible manner.
- Nishio, H. et al. (1996) Gen. Pharmacol. 27, 779.
- Clarke, P.B. et al. (1990) Br. J. Pharmacol. 99, 509.
- Plosker, G.L. and Benfield, P. (1997) CNS Drugs 7, 410.
- Inoue, Y. et al. (1999) Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 53, 283.
Talipexole is an azepine derivative, and acts as an agonist of D2 dopamine pre- and postsynaptic receptors, as well as an α2-adrenoceptor agonist and 5-HT3 receptor antagonist1.
The purpose of Talipexole is to increase dopamine activity in the central nervous system. It inhibits electrically evoked release of dopamine through activation of D2 synaptic autoreceptors located on dopaminergic terminals. It also causes release of acetylcholine and noradrenalin2,3.
Talipexole has been established in a number of clinical trials as an anti-Parkinsonian agent. These trials showed significant improvement in motor activity and in other parkinsonian symptoms including akinesia, rigidity, tremor and gait disturbances. There are several side effects caused by this drug such as drowsiness, dizziness, hallucinations, gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea and loss of appetite3.
In addition, talipexole is also expected to be beneficial for the treatment of periodic leg movement disorder and restless leg syndrome4.
Talipexole dihydrochloride (#B-140) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

