Overview
Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active conjugated peptide toxin.
✓ Localization and distribution
✓ Live cell imaging
✓ Single cell detection
✓ Direct flow cytometry
We gladly take on collaboration projects. Please Contact Us.
Applications
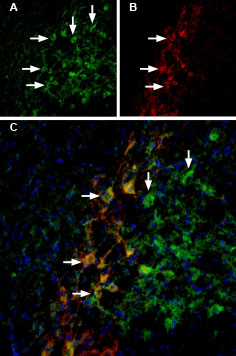 Double staining of GIRK2 channels in substantia nigra pars compacta using Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 and Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody.Rat brain sections were first incubated with 33 nM Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG), (green). The same sections were incubated with Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody (#APC-006-GP). A. Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 binding appears in profiles of substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC) neurons (arrows). B. GIRK2 staining (red) is detected in profiles of SNC neurons (arrows). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates co-staining of GIRK2 channels by Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 and by Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody. DAPI staining (blue) is used to stain nuclei.
Double staining of GIRK2 channels in substantia nigra pars compacta using Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 and Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody.Rat brain sections were first incubated with 33 nM Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG), (green). The same sections were incubated with Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody (#APC-006-GP). A. Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 binding appears in profiles of substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC) neurons (arrows). B. GIRK2 staining (red) is detected in profiles of SNC neurons (arrows). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates co-staining of GIRK2 channels by Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 and by Guinea pig Anti-GIRK2 (Kir3.2) Antibody. DAPI staining (blue) is used to stain nuclei. Alomone Labs Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 binds GIRK1/4-Cherry transfected HEK293T cells.Transfected cells were incubated in the presence of 200 nM Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG). The labeled toxin accumulates on the membrane surface after 26 sec. No binding is achieved in untransfected cells (data not shown).
Alomone Labs Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 binds GIRK1/4-Cherry transfected HEK293T cells.Transfected cells were incubated in the presence of 200 nM Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG). The labeled toxin accumulates on the membrane surface after 26 sec. No binding is achieved in untransfected cells (data not shown).
The pictures are a kind gift from the lab of Prof. Eithan Reuveny, Weizmann Institute, Israel. Direct flow cytometry of Tertiapin-Q in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
Direct flow cytometry of Tertiapin-Q in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM Tertiapin-Q (#STT-170).
___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG). Alomone Labs Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 inhibits Kir3.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A continuous current trace recorded at a holding potential of -80 mV. Kir3.2 currents are downward reflections activated by high K+ containing solution. While activated, 50 nM and 100 nM of Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG) were applied for 2 min (indicated as bars).
Alomone Labs Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 inhibits Kir3.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A continuous current trace recorded at a holding potential of -80 mV. Kir3.2 currents are downward reflections activated by high K+ containing solution. While activated, 50 nM and 100 nM of Tertiapin-Q-ATTO Fluor-488 (#STT-170-AG) were applied for 2 min (indicated as bars).
Citations
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Biological Activity
- Jin, W. and Lu, Z. (1998) Biochemistry 37, 13291.
- Jin, W. et al. (1999) Biochemistry 38, 14294.
- Drici, M.D. et al. (2000) Br. J. Pharmacol. 131, 569.
- Kitamura, H. et al. (2000) Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 293, 196.
Solubility and Storage
Centrifuge the vial before adding solvent (10,000 x g for 5 minutes). The lyophilizate may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Tap the vial to aid in dissolving the lyophilized product. Tilt and gently roll the liquid over the walls of the vial. Avoid vigorous vortexing. Light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed.
Soluble in pure water at high-micromolar concentrations (50 µM - 1 mM). For long-term storage in solution, it is recommended to prepare a stock solution by dissolving the product in double distilled water (ddH2O) at a concentration between 100-1000x of the final working concentration. Divide the stock solution into small aliquots and store at -20°C. Before use, thaw the relevant vial(s) and dilute to the desired working concentration in your working buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations at 10,000 x g for 5 minutes before use. It is recommended to prepare fresh solutions in working buffers just before use. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain biological activity. Avoid exposure to light.
Scientific Background
Tertiapin, the native toxin, was originally isolated from European honey bee Apis mellifera venom. Native and synthetic Tertiapin blocks a range of inward rectifier K+ channels (Kir), in particular ROMK1 (Kir1.1, IC50 = 2 nM) and GIRK (Kir3 family, IC50 for the Kir3.1/3.4 heteromer was 8.6 nM) but with no effect on the Kir2 family member1. In accordance, it was shown to inhibit acetylcholine induced K+ currents in mammalian cardiomyocytes2,3.
Tertiapin-Q is a derivative of Tertiapin in which Met13 is substituted by a Gln residue. However, unlike native Tertiapin, Tertiapin-Q is non-oxidizable and therefore is more stable4.
Tertiapin-Q inhibits the above-mentioned channels with similar affinities and also inhibits Ca2-activated large conductance BK-type K+ channels in a concentration and voltage-dependent manner5.
- Jin, W. and Lu, Z. (1998) Biochemistry 37, 13291.
- Drici, M.D. et al. (2000) Br. J. Pharmacol. 131, 569.
- Kitamura, H. et al. (2000) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 293, 196.
- Peleg, S. et al. (2002) Neuron 33, 87.
- Kanjhan, R. et al. (2005) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 314, 1353.

