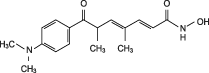
Overview
- Yoshida, M. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17174.
- Yamashita, Y. et al. (2003) Int. J. Cancer 103, 572.
- Donadelli, M. et al. (2003) Mol. Carcinog. 38, 59.
- Tsuji, N. et al. (1976) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 29, 1.
- Yoshida, M. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17174.
- Yoshida, M. et al. (1995) Bioessays 17, 423.
- Hoshikawa, Y. et al. (1994) Exp. Cell Res. 214, 189.
- Futamura, M. et al. (1995) Oncogene 10, 1119.
- Papeleu, P. et al. (2003) J. Hepatol. 39, 374.
- Yamashita, Y. et al. (2003) Int. J. Cancer 103, 572.
- Donadelli, M. et al. (2003) Mol. Carcinog. 38, 59.
- Ailenberg, M. et al. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 298, 110.
- Sawa, H. et al. (2002) Brain Tumor Pathol. 19, 77.
- Shaker, S. et al. (2003) Leuk. Res. 27, 437.
Trichostatin A (TSA), an antifungal antibiotic derived from Streptomyces, is a potent and reversible inhibitor of histone deacetylase.1 TSA causes accumulation of highly acetylated histone molecules in mammalian cells,2 that leads to chromatin relaxation and modulation of gene transcription/expression.3
TSA blocked cell cycle progression at the G1 phase in HeLa cells.4 In NIH 3T3 cells, it induced reversion of oncogenic ras-transformed cells to a normal morphology.5 TSA did not induce apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes,6 however, it induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma cell lines (HepG2, Huh-7).7
Unlike sodium butyrate, Trichostatin A action is very specific and reversible and thus, became a widely used tool to study the consequences of histone acetylation in vitro and in vivo.
TSA strongly inhibited the cellular growth of nine pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. It induced up-regulation of p21 (WAF1/CIP1), cell cycle arrest at G2, and apoptosis. Therefore, TSA may have a potential utility in treatment of pancreatic cancer.8
Recently, TSA was reported as a potent inhibitor of Gelatinase A, a matrix metalloproteinase implicated in metastasis,9 and it also inhibited the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from human glioblastoma cells.10 Preclinical evaluation of TSA in combination with DNA methylation inhibitors, demonstrated a synergistic anti-neoplastic effect against myeloid leukemic cells.11
Trichostatin A (#T-300) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active compound.
Applications
Citations
- Ling, L. et al. (2013) J. Mol. Endocrinol. 50, 279.