Overview
- Khom, S. et al. (2007) Neuropharmacol., 53, 178.
- Benke, D. et al. (2008) Neuropharmacol. 56, 174.
- Khom, S. et al. (2016) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 357, 580.
- Dietz, B.M. et al. (2005) Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 138, 191.
Up to 200 mM in DMSO. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (5,000 x g for 1 min).
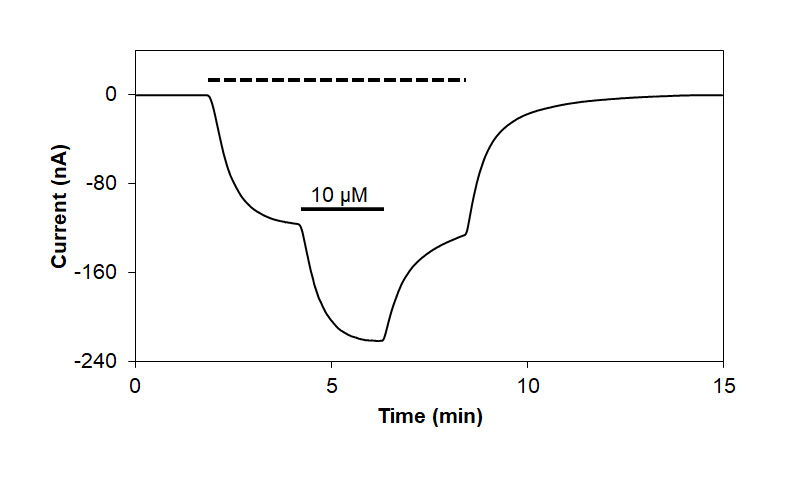 Alomone Labs Valerenic acid activates GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABAA α1/β2 current, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 0.1 µM γ-aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and enhanced by co-application of 10 µM Valerenic acid (#V-140), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -80 mV.
Alomone Labs Valerenic acid activates GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABAA α1/β2 current, activated by a continuous application (top dotted line) of 0.1 µM γ-aminobutyric acid (#G-110), and enhanced by co-application of 10 µM Valerenic acid (#V-140), as indicated (bar), at a holding potential of -80 mV. Alomone Labs Valerenic acid potentiates GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABAA α1/β2 channel current activation by a continuous application of 200 µM Valerenic acid (#V-140), duration indicated by bar (bottom left), compared to activation by 0.1 µM γ-aminobutyric acid (#G-110), at a holding potential of -80 mV.
Alomone Labs Valerenic acid potentiates GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Representative time course of GABAA α1/β2 channel current activation by a continuous application of 200 µM Valerenic acid (#V-140), duration indicated by bar (bottom left), compared to activation by 0.1 µM γ-aminobutyric acid (#G-110), at a holding potential of -80 mV.
- Ramharter, J. et al (2012) EurJOC., 10, 2041.
- Dietz, B.M. et al. (2005) Mol. Brain. Res., 138, 191.
- Lu, Q. et al. (2020) Int. J. Biol. Sci., 16, 2104.
Valerenic acid was first isolated in 1957 from the rhizome and roots of valerian (Valeriana offi-cinalis). Valerian is one of the oldest medicinal herbs in folk medicine and has been used for various afflictions like insomnia, anxiety, and pain. Valerenic acid was found to be pharmacologically active monoterpene acting through binding to the GABAA receptor1.
Valerenic acid acts as an anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting the transcription of NF-κB, one essential transcription factor controlling the expression of numerous inflammation-related genes. In addition, evidence suggests that Valerenic acid acts as an agonist for 5-HT receptors (serotonin receptors), which are G-coupled receptors that mediates neuronal activity via regulating cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels2.
In-vivo studies that conducted on xenograft glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) mice models shown that Valerenic acid induce cell death of GBM cells by inducing AMPK activation. Therefore, Valerenic acid may serve as a potential anti-tumor agent towards GBM patients3.
Valerenic acid (#V-140) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.