Overview
|
| Bioz Stars Product Rating | |
| The world's only objective ratings for scientific research products | |
| Mentions | |
| Recency | |
| View product page > | |
Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody (#APZ-041) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize DLGAP1 from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Applications
 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody (#APZ-041), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody (#APZ-041), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody, preincubated with DLGAP1/GKAP Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PZ041).
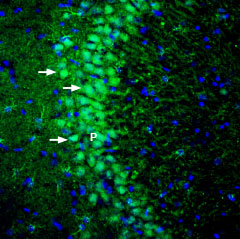 Expression of GKAP in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody (#APZ-041), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. GKAP staining (green) in hippocampal CA3 region is detected in neurons (arrows) of CA3 pyramidal layer (P). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of GKAP in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-DLGAP1/GKAP Antibody (#APZ-041), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. GKAP staining (green) in hippocampal CA3 region is detected in neurons (arrows) of CA3 pyramidal layer (P). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Citations (8)
Specifications
- Peptide (C)KISNEHSPKLQIRSH, corresponding to amino acid residues 397-411 of rat DLGAP1 (Accession P97836). Intracellular.

Scientific Background
DLGAP1/GKAP (discs large homolog associated protein 1/guanylate kinase associated protein) is a member of the DLGAP family, scaffold proteins localized to the postsynaptic density. The protein is involved in signaling to and from glutamate receptors, it serves as a key adaptor protein of NMDA receptors, involved in learning and memory and synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system1,2.
DLGAP family comprises five conserved proteins, DLGAP1–DLGAP5. DLGAP1-DLGAP4 proteins interact directly with both DLG and SHANK through their multiple domains. DLGAP1–4 proteins are implicated in several neurological disorders including schizophrenia, autism, obsessive compulsive disorder and cerebellar ataxia1.
DLGAP1 is highly expressed in the brain; Dlgap1 mRNA is detected in the cortex, hippocampus, olfactory bulb, striatum and thalamus1.
- Rasmussen, A.H. et al. (2017) Mol. Brain 10, 43.
- Li, L. et al. (2018) Cancer Cell 33, 736.
