Overview
- Peptide CKQNKQGANSRPVNQT corresponding to amino acid residues 278-293 of human p75NTR (Accession P08138). Intracellular, juxtamembrane domain.
- Rat brain and A875 human melanoma cells (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody (#ANT-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody (#ANT-011), (1:200).
2. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody, preincubated with p75 NGF Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT011).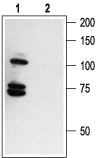 Western blot analysis of human melanoma cells A875:1. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody (#ANT-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human melanoma cells A875:1. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody (#ANT-011), (1:200).
2. Anti-p75 NGF Receptor (intracellular) Antibody, preincubated with p75 NGF Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT011).
- Mouse brain sections.
The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. p75NTR, like all the superfamily members is a type I transmembrane protein with tandem cysteine-rich domains in the extracellular portion and a intracellular death domain. p75NTR binds its ligands as a homodimer but can also form heterodimers with other receptors such as TrkA, TrkB, TrkC, Nogo receptor and sortilin. The precise multimeric receptor complex formed between p75NTR and the other receptors will determine the ligand being recognized (see below) and the biological response to its binding.
As it name implies, p75NTR binds all the neurotrophins (NGF, BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4) with similar nM affinities. Co-expression of p75NTR with the Trk receptors enhances the ability to bind and respond to the specific neurotrophin and induces cell survival. On the other hand, it has recently been demonstrated that p75NTR binds with high affinity to the unprocessed form of NGF (proNGF) probably as a complex with sortilin and this leads to cell death by apoptosis. Finally, a multimeric complex of p75NTR and Nogo receptor binds myelin proteins such as Nogo-66, MAG and OmgP resulting in inhibition of axonal growth.
